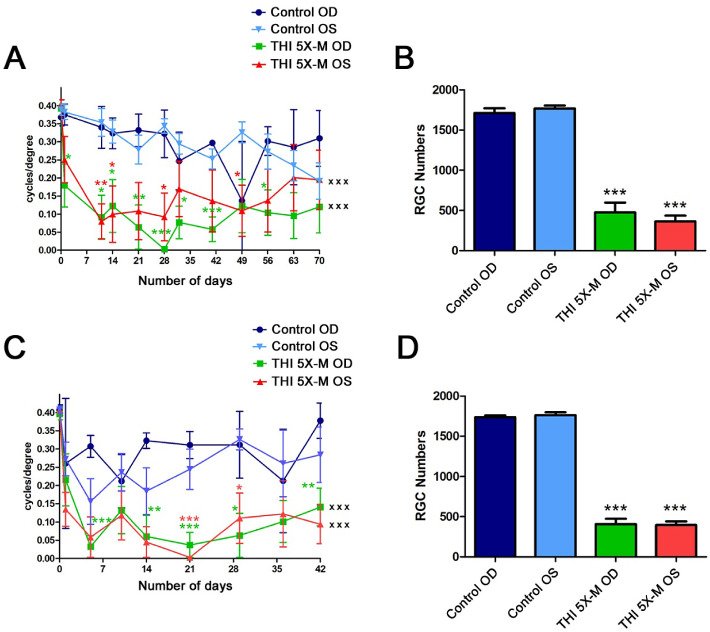
Figure 5.
RGC and vision loss is bilateral. (A) OKR scores compared by repeated-measures ANOVA over 70 days were significantly decreased in right eyes (OD) (n = 4; xxxP < 0.001) and left eyes (OS) (n = 4; xxxP < 0.001) of 5×-M mice compared with right and left eyes of control mice (n = 4), respectively. Decreased OKR scores at individual time points, compared with the corresponding eyes of control mice, were determined by ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). No significant difference was found between right eyes and left eyes within the 5×-M mice over time nor at any individual time points. (B) Brn3a-stained, flat-mounted retinal sections from mice sacrificed on day 70 showed a significant decrease in number of RGCs in both right eyes (n = 4; ***P < 0.001) and left eyes (n = 4; ***P < 0.001) of 5×-M mice compared with corresponding eyes of control mice (n = 4). (C) OKR scores compared by repeated-measures ANOVA over 42 days were significantly decreased in right eyes (n = 4; xxxP < 0.001) and left eyes (n = 4; xxxP < 0.001) of 5×-M mice compared with right and left eyes of control mice (n = 4), respectively. Decreased OKR scores at individual time points, compared with the corresponding eyes of control mice, were determined by ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). No significant difference was found between right eyes and left eyes within the 5×-M mice over time nor at any individual time points. (D) Brn3a-stained, flat-mounted retinal sections from mice sacrificed on day 42 showed a significant decrease in RGC numbers in right eyes (***P < 0.001) and left eyes (***P < 0.001) of 5×-M mice compared with corresponding eyes of control mice. N represents the number of left or right eyes, each plotted as a single data point. Data represent mean ± SEM.