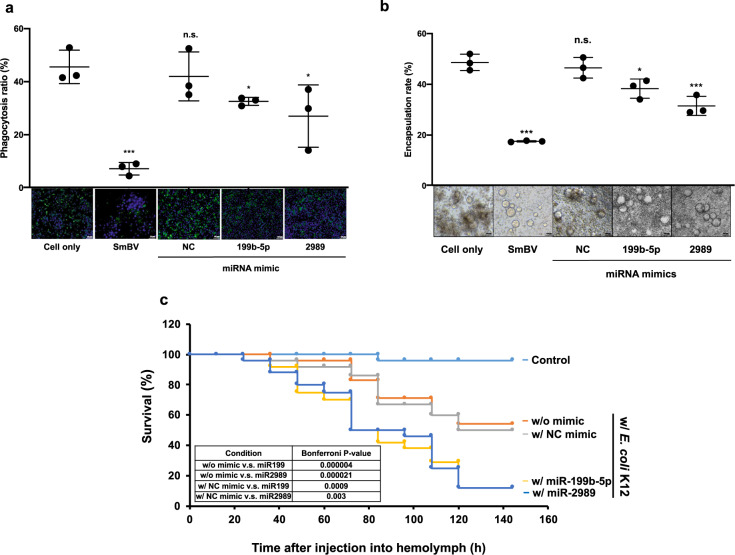
Fig. 4. SmBV-encoded miR-199b-5p and miR-2989 suppress cellular immune responses in S. litura.
Third-instar S. litura larvae were microinjected with SmBV, miR-199b-5p or miR-2989 mimic. a Phagocytosis activity of injected S. litura larvae; green fluorescence is emitted from the ingested E. coli by hemocytes. The phagocytosis ratio (%) was derived from the ratio of FITC to DAPI. (The p-value of SmBV: 0.00210683, NC mimic: 0.30700539, 199b-5p mimic: 0.03159918, 2989 mimic: 0.04655791). b Encapsulation assay showing binding of multiple hemocytes to Sephadex A-25 beads added to the cell culture. The encapsulation rate was calculated by KP assay. Bottom: representative images of the Sephadex A-25 beads added to each cell culture. (The p-value of SmBV: 0.00168336, NC mimic: 0.25959650, 199b-5p mimic: 0.01188009, 2989 mimic: 0.00211812). c Survival rate of larvae in response to infection by E. coli K12. Kaplan–Meier survival curve with log-rank test (Wilcoxon–Breslow–Gehan Test) comparing survival of S. litura larva infected with E. coli K12. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Pairwise comparison: with NC mimic vs. with miR-199b-5p, p < 0.0001; with NC mimic vs. with miR-2989, p < 0.01. NC mimic: negative control mimic. All experiments were performed with five biological replicates (n = 5). Data are expressed as the mean and standard deviation (SD). p-value were calculated using Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.0005).