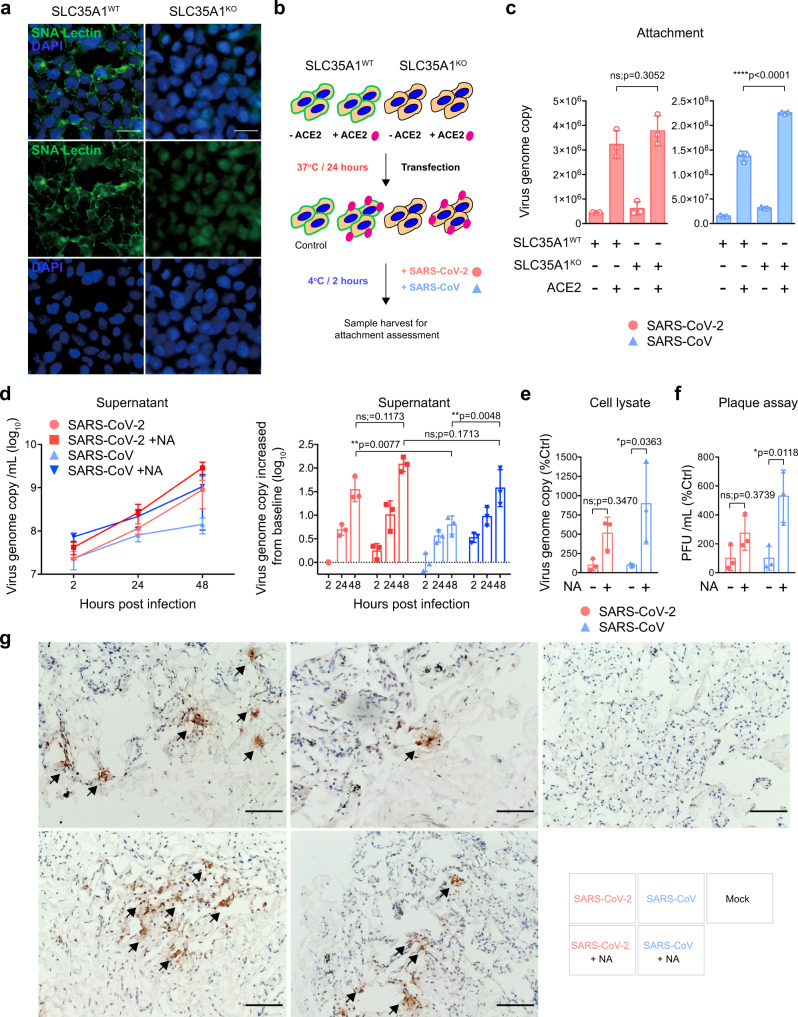
Fig. 3. SARS-CoV-2 partly overcomes sialic acid-mediated restriction in ex vivo human lung tissues.
a SLC35A1WT and SLC35A1KO 293 cells were fixed and stained with Sambucus Nigra Lectin (green) and DAPI (blue) for cell surface sialic acid detection. Bars represented 50 µm. b Schematic of attachment assay. c SLC35A1WT and SLC35A1KO 293 cells with or without hACE2 overexpression were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV at 0.2 MOI for 2 h at 4 °C. Cell lysates were harvested at 2hpi for qRT-PCR analysis (n = 3). d–e Mock- or NA-treated ex vivo human lung tissues were infected with SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV at an inoculum of 1 × 107PFU/ml. Supernatants were collected at 2, 24, and 48hpi and tissue samples were collected at 48hpi for qRT-PCR analysis (n = 3). f Supernatants at 48hpi were titrated by plaque assays (n = 3). g Representative images of human lung tissues challenged with SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV with or without NA treatment. Viral N proteins were detected with anti-SARS-CoV-2-N or rabbit anti-SARS-CoV-N immune serum (arrows). Bars represented 100 µm. Data represented mean and standard deviations from the indicated number of biological repeats. The experiments in a and g were repeated three times independently with similar results. Statistical significance between groups was determined with two way-ANOVA. * represented p < 0.05, ** represented p < 0.01, *** represented p < 0.001, **** represented p < 0.0001. ns not significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.