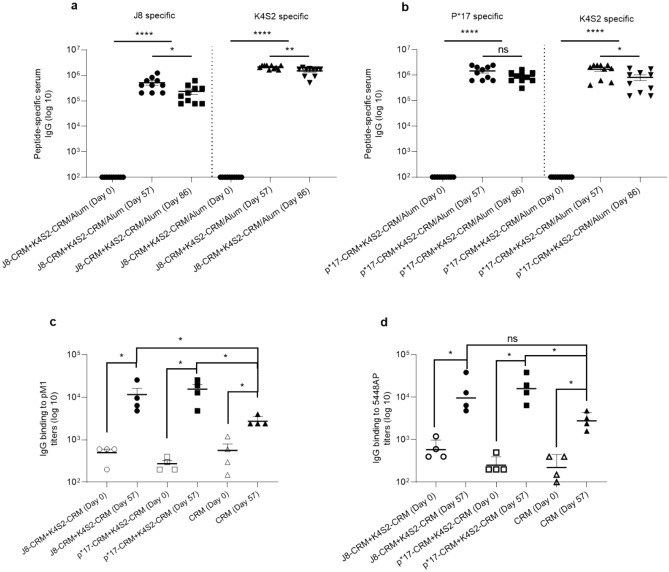
Figure 3.
Vaccine immunogenicity and functionality of vaccine-induced antibodies. (a,b) Vaccine peptide specific serum IgG titers induced in Sprague–Dawley rats after vaccination with J8-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum or p*17-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum. Sprague–Dawley rats were immunized intramuscularly with 0.1 mg/dose of J8-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum or p*17-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum on days 0, 21 and 42. Rats were euthanized at day 57 and day 86. J8, p*17 and K4S2 specific serum IgG titers (Geomean) are shown for individual rats vaccinated with J8-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum (a) or p*17-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum (b) euthanized at day 57 (n = 10; 5 male, 5 female) or 86 (n = 10; 5 male, 5 female). Pre-vaccination (day 0) serum IgG titers of the same rats assessed at day-57 or -87 are also shown. Samples were considered positive when the mean value of the absorbance, of the highest dilution (1:100), was > 3SD above the mean OD of the negative control. (c,d) Strep A surface binding of vaccine induced antibodies. Sera collected from rats vaccinated with J8-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum, p*17-CRM + K4S2-CRM/Alum or CRM/Alum in the toxicology study was assessed for direct IgG binding to heat killed pM1 (c) and 5448AP (d). Mean individual titers of sera collected from days-0 (n = 4) and -57 (n = 4) and assayed by ELISA are shown. Statistical analysis and graphs generated using a Mann–Whitney test to compare all groups, were performed using GraphPad Prism (8.1.2) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.