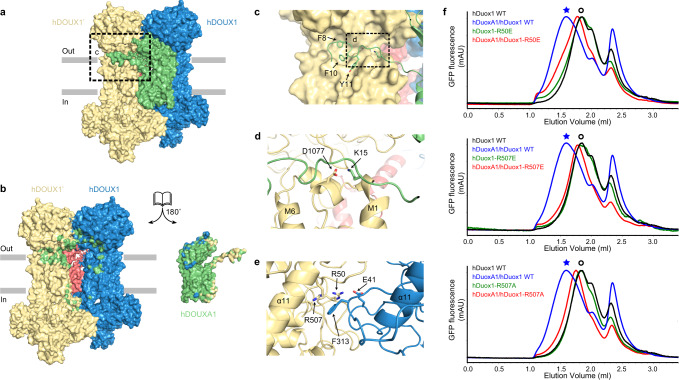
Fig. 4. Mechanism of hDUOX1–hDUOXA1 tetramer assembly.
a The side view of hDUOX1–hDUOXA1 protein complex shown in surface representation and colored the same as in Fig. 1d. b The open-book view of the inter-subunit interfaces. Residues of hDUOX1 subunits that interact with hDUOXA1 subunit are colored in green. Residues of hDUOXA1 subunit that interact with hDUOX1 subunits are colored in yellow and blue. c The close-up view of the interactions between NTP of hDUOXA1 and hDUOX1 boxed in a. d The close-up view of additional interactions between NTP of hDUOXA1 and hDUOX1 boxed in c. e The top view of interactions between PHD of two opposing hDUOX1 subunits. f Representative FSEC traces of hDOUX1 R50E, R507E, and R507A mutants are compared to that of wild-type (WT) hDOUX1. The peak position of the hDOUX1 peak is denoted by the hollow circles. Asterisks denote the peak position of hDUOX1–hDUOXA1 protein complex.