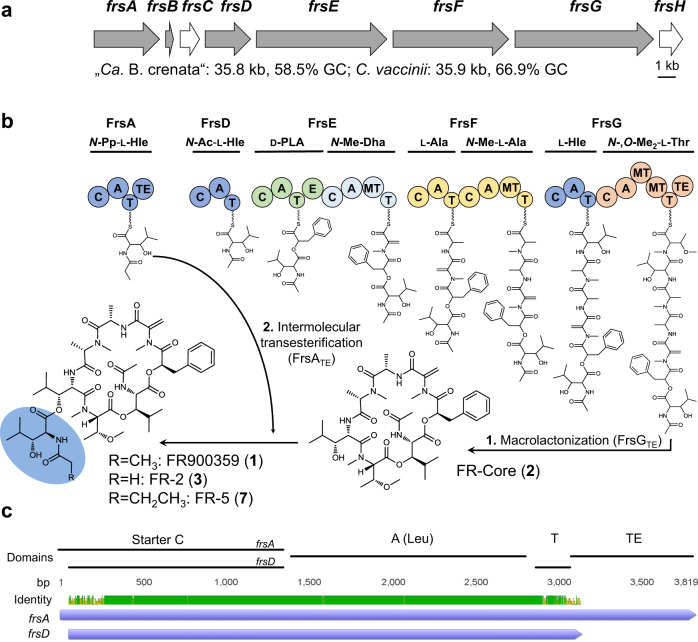
Fig. 1. FR biosynthesis.
a Organization, size and GC content of the frs BGCs from “Ca. B. crenata” and C. vaccinii (gray = NRPS, white = modifying enzyme). b Biosynthetic pathway of 1. First, the NRPS FrsDEFG together with FrsH forms a seven-membered linear peptide chain which is then hydrolyzed and cyclized by FrsGTE to 2. Then, FrsATE catalyzes intermolecular transesterification of N-Pp-Hle synthesized by FrsACAT and FrsH (see Fig. 3a) onto 2 to yield the final product 1 (or 3). Pp = Propionyl, Ac = Acetyl, Me = Methyl, Hle = l-3-Hydroxyleucine, PLA = Phenyllactic acid, Dha = Dehydroalanine. Domains are abbreviated as: C = condensation A = adenylation, T = thiolation, E = epimerization, MT = methyl transferase. Modules are colored according to their activated amino acid precursors. c Nucleotide alignment of frsA and frsD. All predicted domains and identity are indicated. Prediction of domains was conducted with InterPro (EMBL).