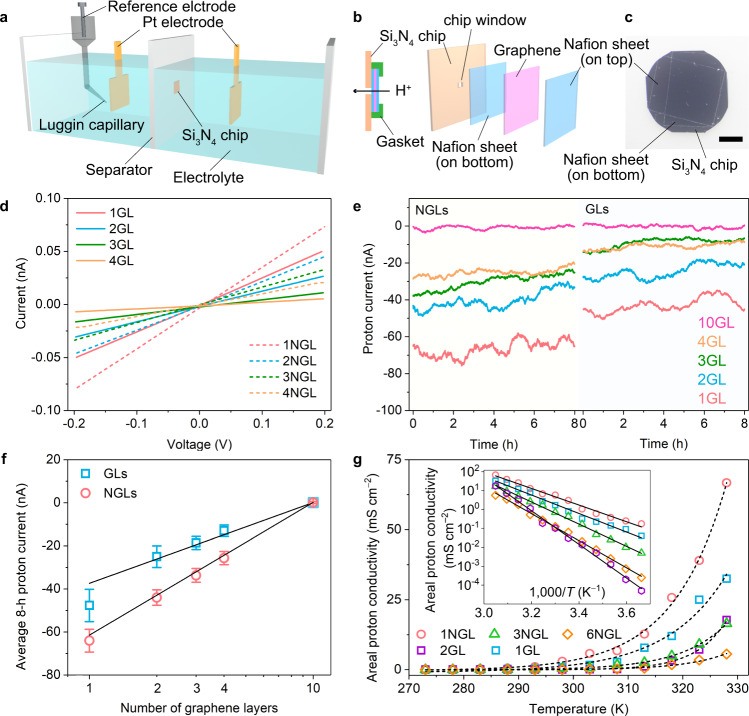
Fig. 3. H-type cell fabrication and electrochemical data for proton penetration through graphene layers.
a Schematic of the H-type cell. b Placement of a stacked Nafion/graphene/Nafion sandwich membrane over the window area of a Si3N4 chip. Nafion acts as a protective sheet for graphene layers with high proton conductivity, chemical/electrochemical stability, and extremely low electron conductivity43. All gaps and points of connection were sealed by an acid-stable, ion-impenetrable gasket to ensure that protons could only pass through the graphene on the window area. c Optical photographic image of the Si3N4 chip with an attached Nafion/graphene/Nafion sandwich. d I–V characteristics of the proton penetration through non- and N-doped graphene membranes with one to four layers. The solid and dashed curves represent the proton currents observed through GLs and NGLs, respectively. e Proton currents collected by CA at a cathode potential of −20 mV vs. RHE through the GLs and the NGLs. f Average proton currents collected during 8 h of CA testing. Error bars show the fluctuations in the measured signals. g Temperature dependences of proton conductivity for 1GL, 2GL, 1NGL, 3NGL, and 6NGL. Inset of (g): log σ as a function of T−1. The solid and dashed curves represent the fits to the experimental results.