Figure 1.
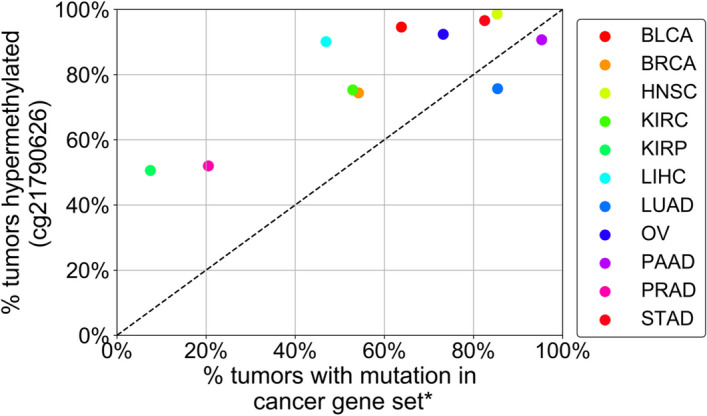
Percentage of tumors that displayed ZNF154 hypermethylation at the probe cg21790626 versus percentage of tumors that displayed mutations in a set of cancer-associated genes for the given cancer type. The percent tumors with a mutation in a cancer gene set on the x-axis are the fraction of tumors that have a mutation in any of the cancer genes of the associated cancer gene set. Methylation data were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas and mutation data were obtained from cBioPortal. *A cancer-associated gene was included in a set if it was listed in the OncoKB database and expected to be recurrently mutated in > 10% of samples for a given tumor type, based on cBioPortal mutation frequencies. Lists of cancer associated genes for each cancer type are located in Table 3. BLCA bladder urothelial carcinoma (n = 130), BRCA breast invasive carcinoma (n = 664), HNSC head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (n = 510), KIRC kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (n = 263), KIRP kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (n = 267), LIHC liver hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 373), LUAD lung adenocarcinoma (n = 185), OV ovarian carcinoma (n = 302), PAAD pancreatic adenocarcinoma (n = 150), PRAD prostate adenocarcinoma (n = 498), STAD stomach adenocarcinoma (n = 349).
