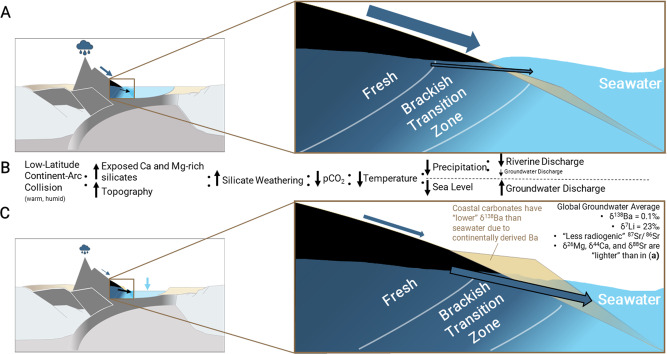
Fig. 4. Illustration of a subterranean estuary during a shift to glacial conditions.
a Interglacial stage steady-state conditions with the subterranean estuary magnified on the right. b Conceptual outline of the feedback outlined by Macdonald et al.11, where a low-latitude island arc collision instigates the onset of global cooling. c Glacial conditions with less precipitation and falling sea level with the subterranean estuary magnified on the right and a description of the chemical changes that might occur to the isotopic composition of global groundwater-derived solute fluxes. The tan triangle represents coastal carbonate deposits, whose δ138Ba composition may be lighter than seawater values if previously exposed to terrestrial (groundwater and river water) runoff.