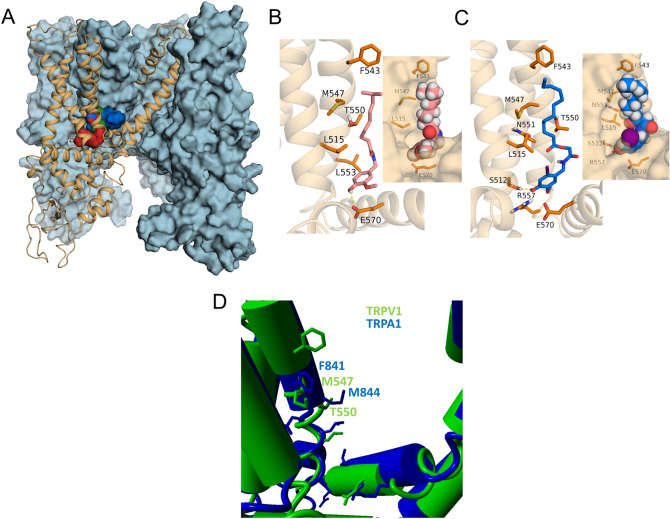
Figure 4.
AG1529 binds to the capsaicin binding site in TRPV1. (A) Transmembrane view of rat TRPV1 structure with three subunits shown as blue surface and one as orange cartoon. For global blind docking assay capsaicin (red surface), capsazepine (green surface) and AG1529 (blue surface) displayed the same binding pocket which corresponds to the capsaicin binding site compressed between helices S3, S4 and the S4–S5 linker. (B) Capsaicin (reddish sticks) orientation in its binding site explored through local docking assay. VDW interactions are observed within capsaicin tail and residues L515 (S3), F543, M547, T550 and L553 (S4). Hydrogen bond is formed between capsaicin head and E570 from the S4-S5 linker. In the inset capsaicin is represented as spheres and the receptor as surface. (C) AG1529 (blue sticks) adopted the same orientation as capsaicin and displayed the same VDW interactions but formed a hydrogen bond with S512. In the inset AG1529 is represented as spheres, where the purple one stands for iodine group and receptor is shown as surface. It can be observed the conformation limitation the head of AG1529 experiments. (D) Structural view of the capsaicin binding pocket of TRPV1 (green) aligned with TRPA1 (blue). Notice that the M844 side chain of TRPA1 is oriented to the central binding cavity sterically perturbing the accessibility of this site to AG1529. Up to 82% of AG1529 docking trials in TRPA1 failed.