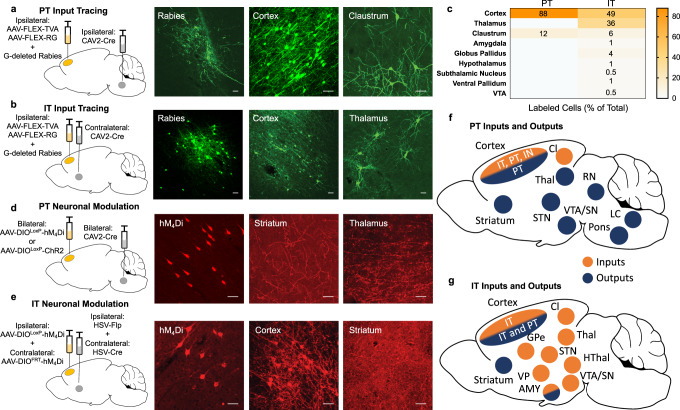
Fig. 1. PT and IT neurons in ACC have distinct inputs and outputs.
a, b Viral strategy using a modified rabies system for monosynaptic retrograde tracing in PT (a) or IT (b) neurons. Retrograde CAV2-Cre virus was injected unilaterally into the pyramidal tract (a) or the dorsomedial striatum (IT) and Cre-dependent TVA and RG vectors were infused into the ipsilateral ACC along with a modified EnvA G-deleted rabies-eGFP. Representative images of GFP-tagged rabies immunofluorescence in PT (a, left panel) and IT (b, left panel) neurons at the site of infection in the cortex, PT inputs from cortex and claustrum (a, middle and right panels), and IT inputs from cortex and thalamus (b, middle and right panels). These regions represent the two strongest inputs into PT (a) and IT (b) cells. Scale bars, 50 µm. c Summary of the relative input strength (by %) to PT and IT neurons in the ACC. Data from 25 PT cells and 315 IT cells. d, e Viral strategy for targeting transgenes bilaterally to PT (d) or IT (e) neurons. For PT neurons (d), CAV2-Cre was injected bilaterally into the pyramidal tract and a Cre-dependent hM4Di or ChR2 virus was injected bilaterally into the ACC. For IT neurons (e), retrograde HSV-Cre and HSV-Flp viruses were injected unilaterally into opposite hemispheres of dorsomedial striatum and the complementary Cre-dependent or Flp-dependent hM4Di virus was infused unilaterally into the contralateral ACC. Representative images of mCherry-tagged hM4Di immunofluorescence in PT (d, left panel) or IT (e, left panel) neurons in cortex, PT terminals in striatum and thalamus (d, middle and right panels), and IT terminals in cortex and striatum (e, middle and left panels). The cortex image in e (middle panel) also shows hM4Di-labeled IT cell bodies because of contralateral IT projections. Scale bars, 50 µm. f, g Summary of the known PT (f) and IT (g) inputs and outputs. PT neurons have diverse outputs, but a restricted source of inputs originating in cortex and claustrum whereas IT neurons have a restricted set of outputs to contralateral cortex, striatum, and amygdala, but a diverse set of inputs.