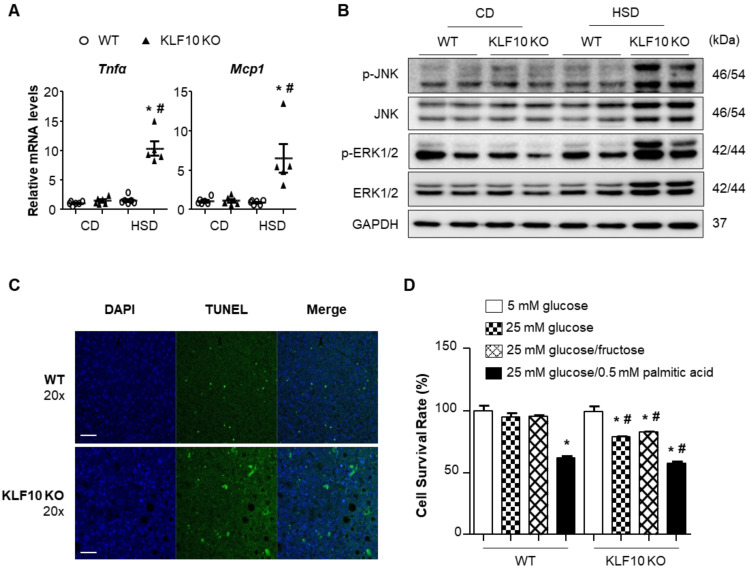
Figure 5.
High sucrose diet activates stress-mediated inflammation and cell death in Klf10 KO mouse livers. Eight-week-old WT and Klf10 KO mice were fed either CD or HSD for eight weeks (n = 5–6 mice/group). (A) Relative mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines Tnfα and Mcp1 in the liver were analyzed via qPCR. * p < 0.05 vs. genotype-matched, CD-fed group and # p < 0.05 vs. diet-matched, genotype control. (B) Western blot analysis of p-JNK, JNK, p-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2, in the livers of WT and Klf10 KO mice fed either CD or HSD. (C) Representative images of the TUNEL assay were used to confirm the induction of apoptosis in the liver sections (Scale bars: 50 μm, Magnification: 20×). (D) Primary hepatocytes were isolated from WT and Klf10 KO mice. The CCK-8 assay determined the cell viability of primary hepatocytes following treatment with 5 mM glucose, 25 mM glucose, 25 mM glucose/fructose, or 25 mM glucose with 0.5 mM palmitic acid for 24 h. * p < 0.05 vs. 5 mM glucose group. # p < 0.05 vs. treatment-matched. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SEM. Charts were produced using GraphPad Prism 5.0. Statistical differences were determined by two-way ANOVA with Mann–Whitney U test using SPSS v17.0. WT, wild type; KO, knockout; CD, control chow diet; HSD, high-sucrose diet, CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8.