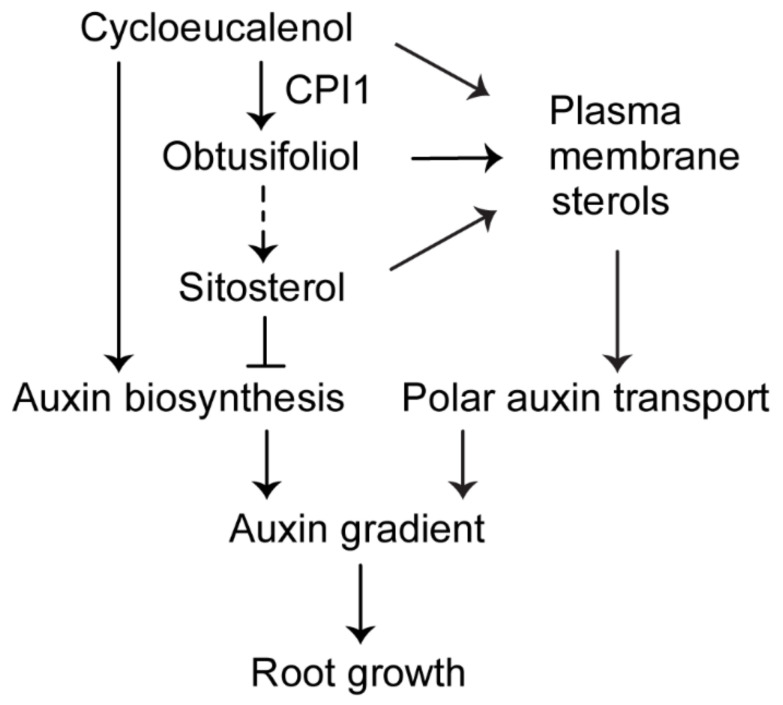
Figure 7.
A working model for the role of CPI1 in Arabidopsis root growth. In the plant sterol biosynthesis pathway, CPI1 catalyzes the conversion of cycloeucalenol into obtusifoliol, which is further metabolized to sitosterol. Cycloeucalenol upregulates the expression of auxin biosynthesis genes; by contrast, sitosterol represses the expression of these genes. Normal content of cycloeucalenol and sitosterol is important for optimal auxin biosynthesis, and correct plasma membrane sterol composition is required for normal polar auxin transport. Auxin biosynthesis and polar auxin transport cooperatively establish an optimal auxin gradient in the root tip to regulate root growth.