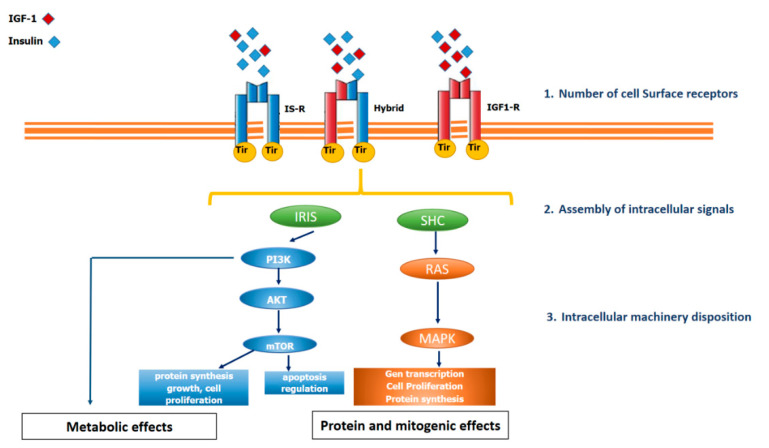
Figure 2.
IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and hybrid receptor. The insulin receptor (IS-R), the insulin-like growth factor receptor type I (IGF-1-R) and the hybrid receptor belong to the family of receptor tyrosine kinases. The figure shows a certain degree of functional overlap. After binding ligands, the receptors stimulate the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues, which then induces phosphorylation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS) and SHC, which dock proteins for activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K-Akt) pathway or the Ras/MAPK pathway, respectively. The PI3K-Akt pathway is predominantly involved in metabolic actions (glucose uptake, insulin sensitivity) and cell proliferation, whereas the RAS/MAPK pathway, is primarily involved in mitogenic effects (proliferation, growth). The number of receptors alone is not the only determining factor in IGF-1 function. In this regard, the assembly and intracellular machinery disposition are also involved.