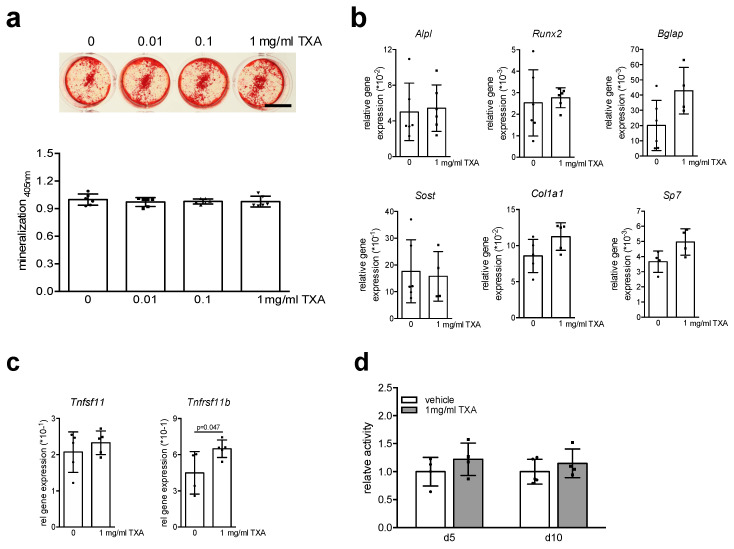
Figure 1.
TXA does not affect the differentiation or function of calvaria-derived osteoblasts. (a) Representative alizarin red stainings of calvaria-derived osteoblasts from WT mice differentiated in the presence of indicated concentrations of TXA for 10 days in osteogenic medium. Scale bar 10 mm. The quantification of extracellular matrix mineralization is indicated below. (b) qRT-PCR expression analysis for the indicated genes in calvaria-derived osteoblasts at day 10 of osteogenic differentiation, stimulated with TXA (1 mg/mL) during the entire course of cell differentiation. (c) qRT-PCR expression analysis for the indicated genes in the same samples. (d) MTT proliferation assay of calvaria-derived osteoblasts stimulated with 1 mg/mL TXA for 6 h at the indicated days of differentiation. For (a–d), n = 4–6 independent cultures per group were used, as indicated by individual data points. Data presented are means ± SD. Gene abbreviations: runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), osterix (Sp7), alkaline phosphatase (Alpl), alpha-1 type I collagen (Col1a1), osteocalcin (Bglap), sclerostin (Sost), Rankl (Tnfsf11), osteoprotegerin (Tnfrsf11b).