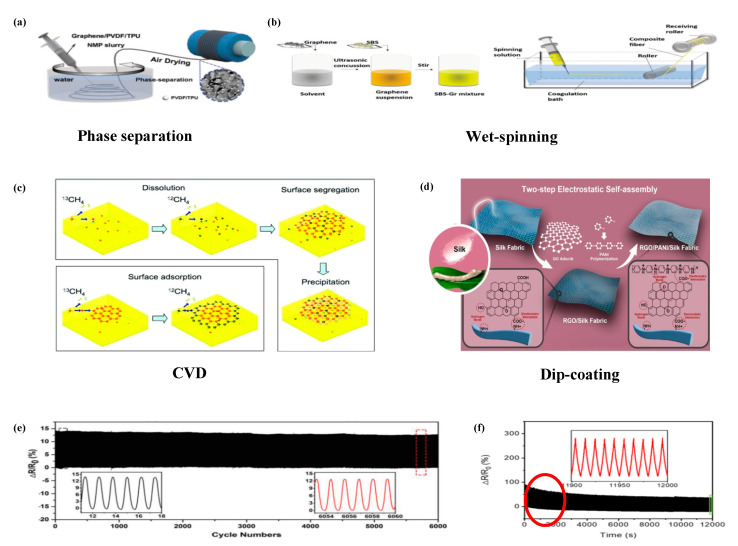
Figure 3.
Fabrication and performance of graphene-based textile strain sensors. (a) Schematic illustration showing the fabrication of PGFs via a phase separation method. “Adapted with permission from reference [57]. Copyright [2019], Advanced Functional Materials”. (b) Schematic illustration for preparing poly (styrene-butadiene-styrene)/graphene composite fibers through a wet-spinning method. “Adapted with permission from reference [45]. Copyright [2020], Macromolecular Materials and Engineering”. (c) Durability of the PGFs strain sensors after 6000 cycles at a 1% strain stretch and release. “Adapted with permission from reference [57]. Copyright [2019], Advanced Functional Materials”. (d) Stability of the rGOFF strain sensor under a repeated applied strain of 20.0%. “Adapted with permission from reference [46]. Copyright [2019], ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces”. (e) Schematic diagram of CVD method. “Adapted with permission from reference [107]. Copyright [2009], Nano Letters”. (f) Schematic diagram of dip-coating method. “Adapted with permission from reference [108]. Copyright [2020], ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces”.