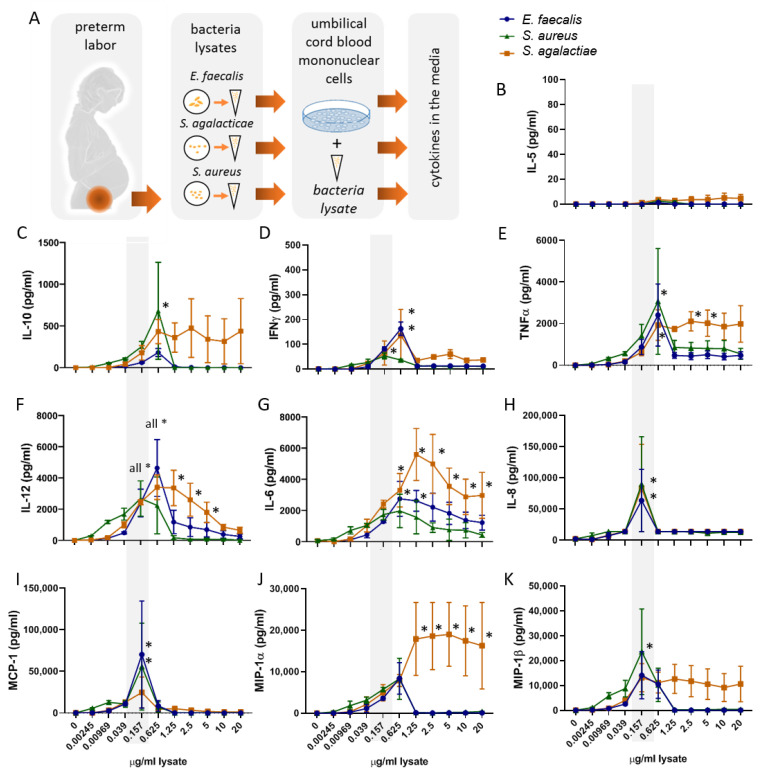
Figure 1.
Experimental setup and optimization of umbilical blood mononuclear cells and bacteria lysate stimulation conditions: in our experimental design (A) vaginal and cervical bacteria samples from women with impeding preterm labor were collected. E. faecalis, S. agalacticae, and S. aureus were isolated and cultured to produce bacteria lysates. Umbilical blood mononuclear cells (UBMC) from ten term-born infants were stimulated in triplicates for 36 h with or without the respective bacterial lysates. The levels of preselected cytokines and chemokines were determined in the supernatants. (B–K) Increasing concentrations of bacteria extract (0.00245–20 µg/mL lysate) were tested for the induction of ten cytokines (IL-5, IL-10, IFNγ, TNFα, IL-12, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, MIP-1α, und MIP-1β), detected using luminex technology. With exception of IL-5 (B), the bacteria lysates significantly induced cytokine secretion (C–K) (two-way ANOVA p < 0.05). * p < 0.05 in Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Concentrations of 0.157 µg lysate/mL (grey shadow) were selected for further experiments. IL-12 refers to IL12p40/70. The three bacteria are depicted as follows: E. faecalis (blue circles), S. agalacticae (orange squares), and S. aureus (green triangles).