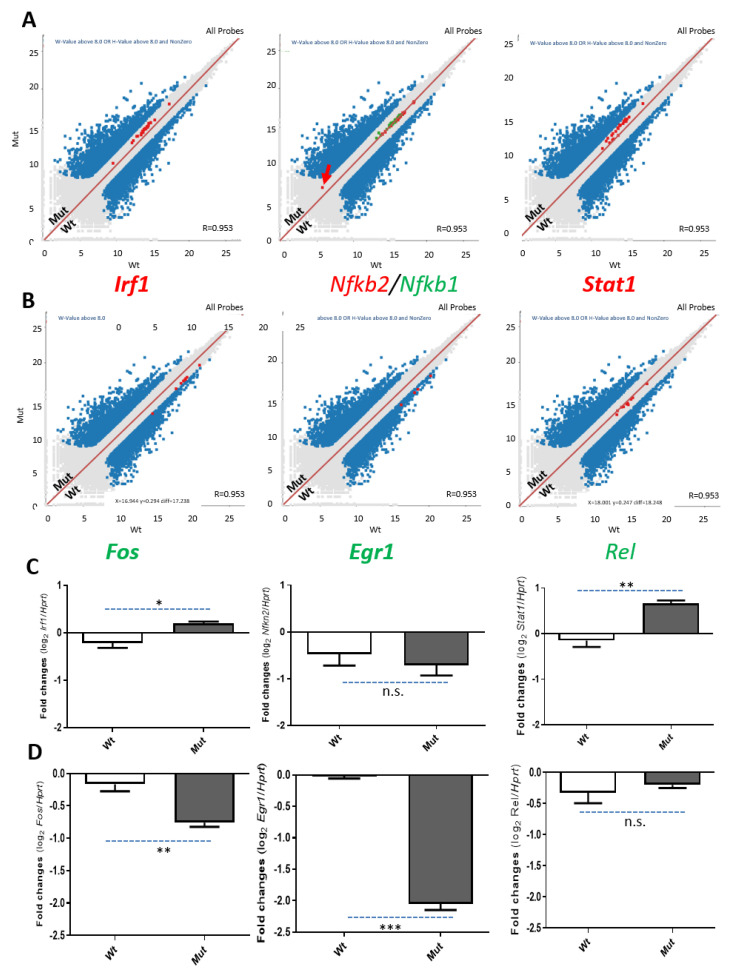
Figure 6.
The NF-κB pathway is the link between the effects of the loss of TSPO on mitochondria and changes in nuclear gene expression. (A). Up-regulation of three genes involved in the NF-κB pathway: Irf1, interferon regulatory factor 1, and the whole set of Irf1 exons are up-regulated as an early actin-rearrangement-inducing factor gene; Nfkb2/1, nuclear factor kappa B subunit 2/1, and one of the Nfkb1 exons (exon 1, indicated in red arrow) are dramatically up-regulated, indicating there is an isoform-specific change; and Stat1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, and all of the Stat1 exons are up-regulated as a whole gene. (B). Down-regulation of three genes involved in the NF-κB pathway: Fos, a proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit (with Jun); Egr1, early growth response protein 1; and Rel, REL proto-oncogene and NF-κB subunit. All of the genes from the NF-κB signaling pathways were selected from the NF-κB Signaling Pathway RT2 Profiler™ PCR Array PAMM-025Z (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). (C,D). Real-time PCR of the six genes shown in A and B. Both Irf1 and Stat1 up-regulation and Fos and Egr1 down-regulation in Tspo Mut cells were confirmed. n.s., non-significant; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001; Student’s t-tests (n = 3).