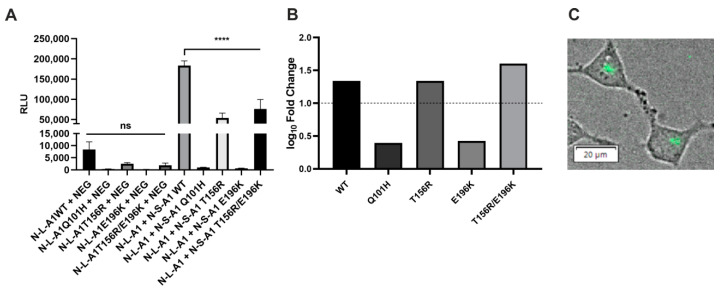
Figure 10.
Analysis of dimerization of the CST variants using the NanoBiT approach. (A) RLU values obtained for the selected protein combinations and the corresponding negative controls. RLU, relative luminescence units; N-S-, protein tagged with SmBiT at the N-terminus; N-L-, protein tagged with LgBiT at the N-terminus; A1, SLC35A1; NEG, HaloTag tagged with SmBiT. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons and are presented as a mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three technical replicates. ns, not significant; p < 0.001 ****. Representative data from two biological replicates with similar tendencies are shown. (B) Decimal logarithms of the ratios calculated by dividing a mean luminescence obtained for the tested combination by a mean luminescence obtained for the corresponding control. The dashed line marks a level of a 10-fold increase (log10 fold change equal 1) of signal over control which sets a threshold of significance suggested by the manufacturer. (C) Bioluminescent imaging of the wild-type CST homodimerization in living HEK293T cells. The NanoLuc-derived luminescence (green) was merged with a brightfield image. Concentrated perinuclear localization of the signals strongly suggests that the CST monomers localize to and interact within the Golgi apparatus.