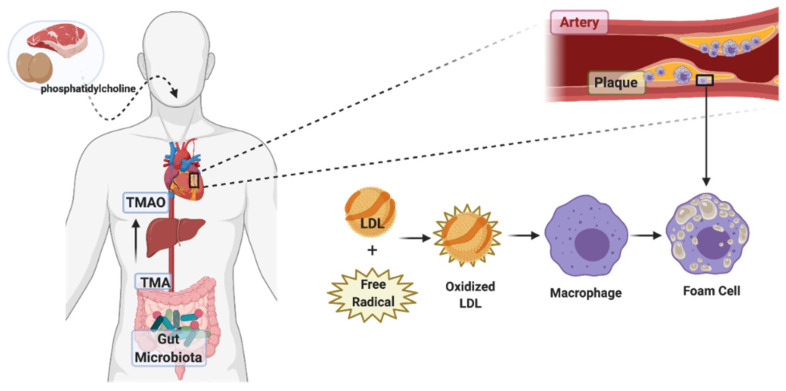
Figure 2.
Role of trimethylamine N-oxide in atherosclerosis. Schematic pathway of phosphatidylcholine transformation to TMA and TMAO (trimethylamine N-oxide) via the gut microbiota. Dietary intake of foods like red meat and egg can alter the composition of gut microbiota. It can result in increased TMA production levels, subsequently leading to increased TMAO synthesis in the liver, eventually leading to elevated levels of oxidized LDLs and increased plaque formation. Accumulated foam cells in the plaques are lipid-laden Macs that have ingested modified lipoproteins, having a foamy appearance. In atherosclerosis, inflammatory Macs are converted into foam cells.