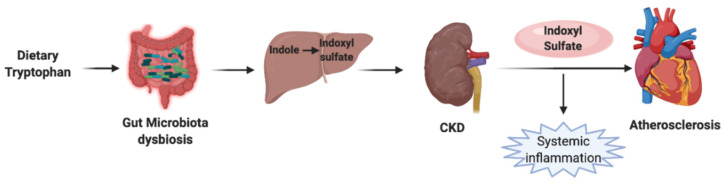
Figure 3.
Effect of Indoxyl sulfate in atherosclerosis. Schematic presentation of the Indoxyl sulfate pathway is linked to atherosclerosis. Tryptophan is metabolized by the gut microbiota into indole, and indole is absorbed into the circulation. In the liver, indole is metabolized to indoxyl sulfate. In chronic kidney disease and dysbiosis conditions, kidneys are incapable of clearing indoxyl sulfate. This results in the accumulation of indoxyl sulfate. Systemic inflammation caused by indoxyl sulfate can cause coronary calcification and chronic cardiovascular abnormalities, eventually leading to atherosclerosis.