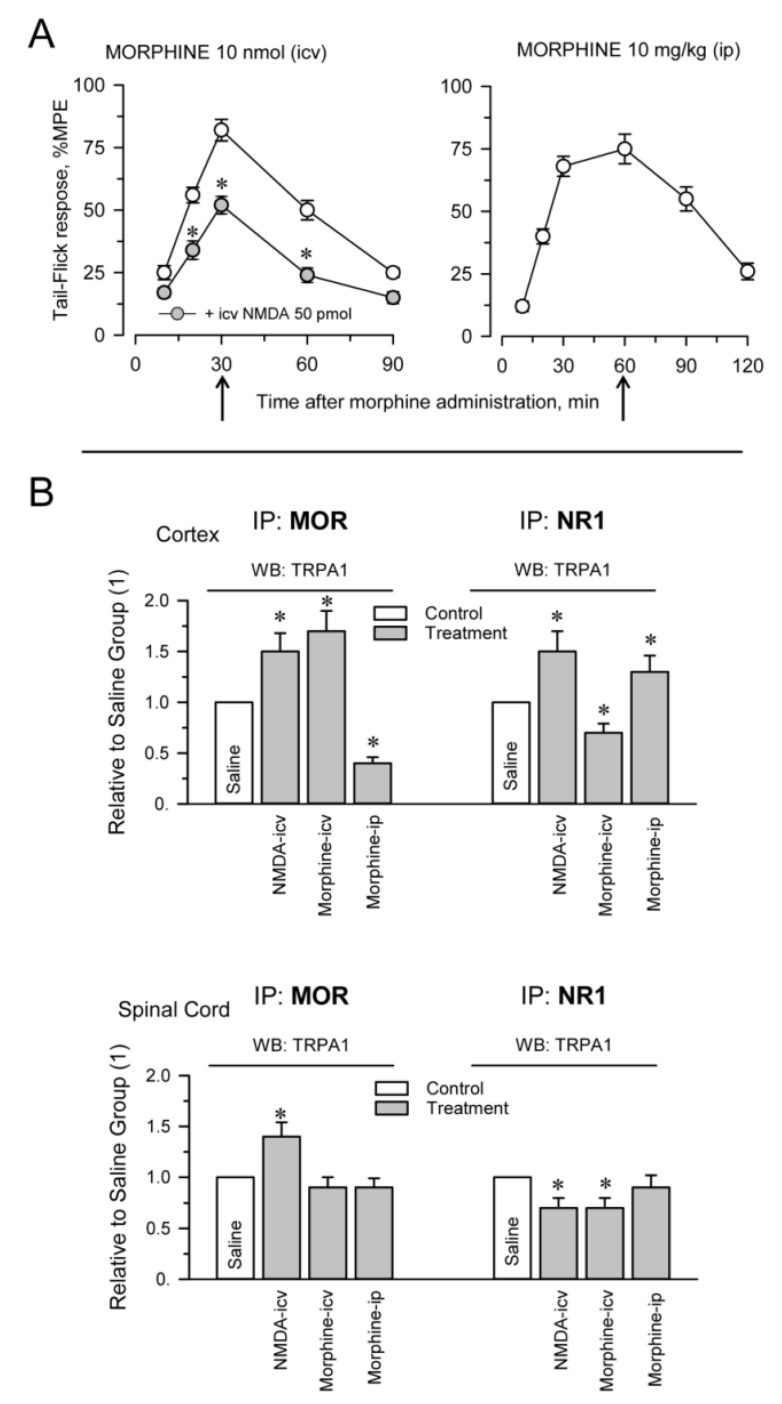
Figure 2.
Pharmacological modulation of TRPA1 associations with MORs and glutamate NMDARs. Different groups of mice were icv-injected with saline, 50 pmol NMDA and 10 nmol morphine. Another group of mice received 10 mg/kg morphine via the ip route. (A) Antinociception promoted by morphine was determined in the warm water tail-flick test and is shown as a time-course. The effect of NMDA is shown relative to its antagonism of icv morphine analgesia. The points are the mean ± SEM from groups of six mice. * Significant differences with respect to the group that received only morphine icv, p < 0.05. (B) Effect of pharmacological interventions on the associations of TRPA1 with MORs and NR1 subunits. Thirty minutes after the icv injections and 60 min after ip morphine (indicated by the arrows), the mice were killed and cortical and spinal cord synaptosomal fractions were prepared. Following solubilization of these membrane preparations, MORs and NR1 subunits were immunoprecipitated. The coprecipitated TRPA1 was detached from the bait proteins and the presence of the monomer was analyzed by Western blotting. For each association and structure, namely, the cerebral cortex and spinal cord, the data were referred to the control group that received saline and was assigned an arbitrary value of 1. The bars are the mean ± SEM from two or three determinations. * Significant differences with respect to the control group, p < 0.05. Further details in Supplementary Materials Figure S4 and Section 4.