Table 2.
Di-substituted coumarins and their CAR activation.
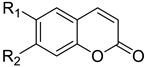
| ||||
| Compound | R1 | R2 | CAR Activation Fold a | Ref |
|
35
esculetin |
OH | OH | −22% ± 12% | [36,44] |
| 36 | methyl | methyl | −17% ± 5% | [24] |
|
37
isoscopoletin |
OH | O-methyl | −10% ± 6% | [45] |
|
38
scopoletin |
O-methyl | OH | −1% ± 5% | [44] |
|
39
scoparone |
O-methyl | O-methyl | - | [15,17] |
|
40
ayapin |
-OCH2O- | 7% ± 2% | [46] | |
| 41 | -OCH2CH2O- | −50% ± 9% | [47] | |
| 42 | O-ethyl | O-ethyl | −26% ± 8% | [37] |
| 43 | O-acetyl | O-acetyl | −11% ± 2% | [37] |
| 44 | O-allyl | O-allyl | −18% ± 15% | New |
| 45 | O-propyl | O-propyl | −37% ± 5% | [37] |
| 46 | O-n-butyl | O-n-butyl | −39% ± 13% | New |
| 47 | O-pentyl | O-pentyl | −10% ± 18% | New |
| 48 | O-isopentyl | O-isopentyl | −61% ± 2% | New |
| 49 | O-hexyl | O-hexyl | −5% ± 9% | New |
| 50 | O-prenyl | O-prenyl | 50% ± 1% | [48,49,50] |
| 51 | O-geranyl | O-geranyl | −32% ± 11% | New |
|
52
isoscopolin |
O-Glc | O-methyl | 35% ± 5% | [17,51] |
|
53
scopolin |
O-methyl | O-Glc | 17% ± 26% | [17] |
a CAR activation fold was calculated: (the luminescence value of the tested compound- the luminescence value of scoparone)/the luminescence value of scoparone (as positive control) × 100%.
