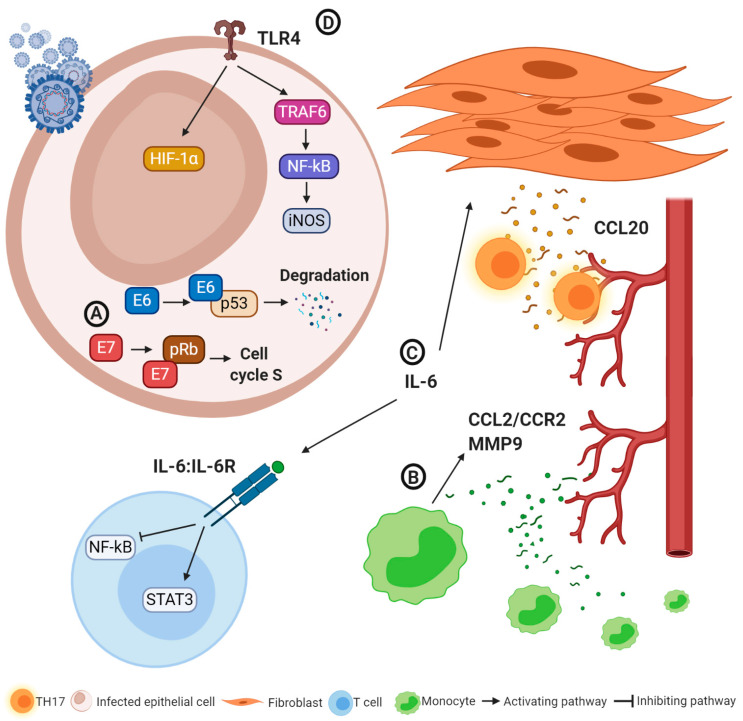
Figure 2.
Oncogenic and immune escape mechanisms in human papilloma virus (HPV)-related tumors. (A) E6 and E7 proteins contribute to averting apoptosis of infected cells and promoting cell proliferation, paving the way for neoplastic transformation. (B) IL-6 reduces the anti-tumoral activity of T lymphocytes and promotes CCL20 expression by cancer-associated fibroblasts and T helper 17 recruitment, also promoting cancer progression. (C) CCL2/CCR2 and MMP-9 production lead to monocyte infiltration and angiogenesis. (D) TLR4 activation promotes cancer progression through HIF-1α induction and nitric oxygen synthesis. Abbreviations: CCL2 and 20: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 and 20; CCR2: C-C chemokine receptor type 2; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IL 6: interleukin 6; IL6R: interleukin 6 receptor; iNOS: inducible nitric oxygen synthase; MMP-9 matrix-metalloproteinase 9; NFkB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; pRB: retinoblastoma protein STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription; TH17: T helper 17; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4, TRAF6: tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6.