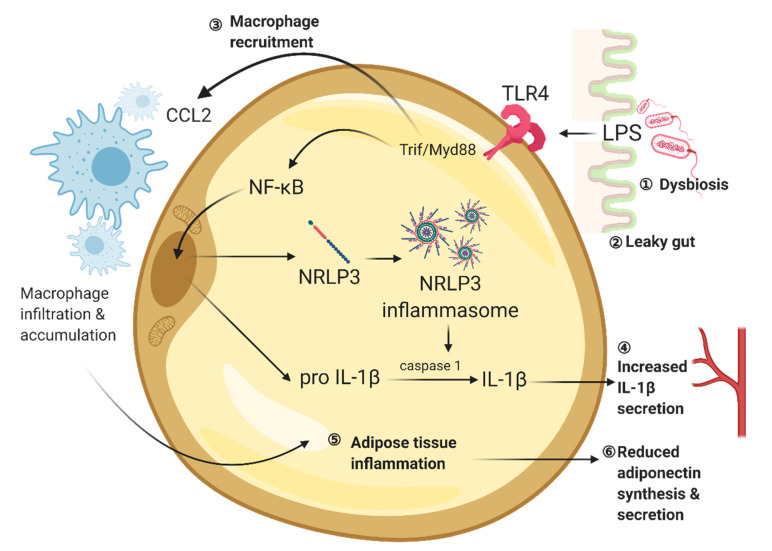
Figure 1.
The high-fat diet promotes gut dysbiosis and adipose tissue inflammation. ① The chronic high-fat diet consumption upset the gut microbiome with an increased ratio of gram-negative bacteria to gram-positive bacteria. ② Endotoxemia reduces endothelium integrity, which allows the leakage of endotoxin, such as lipopolysaccharides. ③ LPS-induced activation of TLR4/Trif/MyD88 promotes macrophage recruitment through the secretion of CCL2. ④ Meanwhile, the activation of TLR4 also promotes NRLP3 and pro IL-1β syntheses, facilitating caspase 1-mediated IL-1β formation. ⑤ In obesity, adipose tissue macrophages further infiltrate and accumulate in the fat tissue results in chronic, low-grade inflammation, while ⑥ adiponectin synthesis and secretion are reduced. Created with BioRender.com.