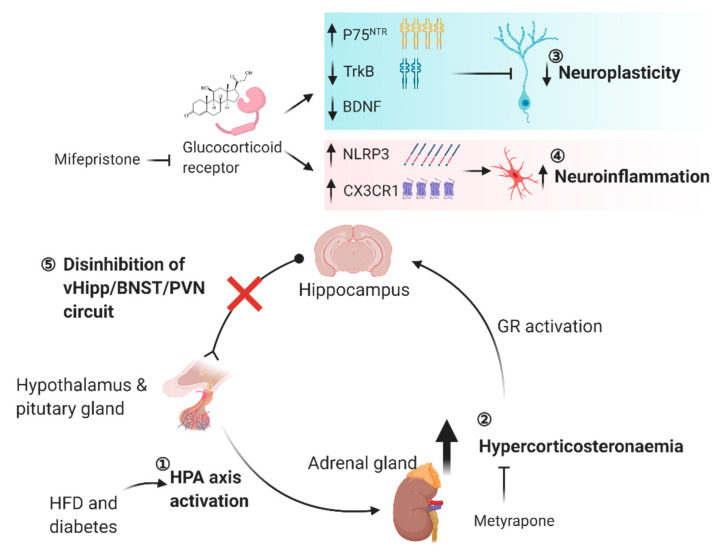
Figure 3.
Obese and diabetic conditions disinhibit the hippocampal inhibitory control over the HPA axis. ① HPA axis hyperactivation is reported in diet-induced obese and diabetic conditions, resulting in ② increased corticosterone synthesis and secretion. Corticosterone can cross the blood-brain barrier and activates the glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus. The activation of the glucocorticoid receptor ③ impairs neuroplasticity and ④ promotes neuroinflammatory response. ⑤ The hippocampus is shown to inhibit the HPA activity through the vHipp/BNST/PVN neural circuit pathway, whereas dysregulated hippocampal plasticity may disinhibit the HPA axis and aggravates the diet-induced hyperactivation of the HPA axis. Created with BioRender.com.