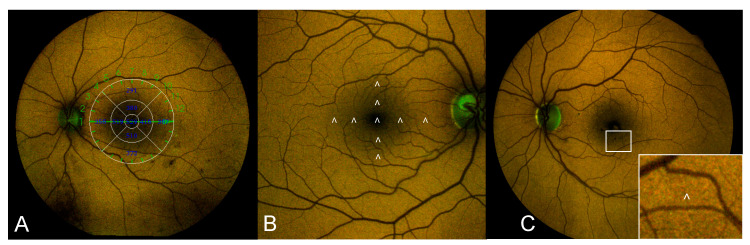
Figure 1.
Example image showing the methodology used for color-FAF quantitative analysis. (A) Color-FAF of the posterior pole of a patient affected by DM and DR with superimposed standard ETDRS grid used as a reference for the identification of the 9 quadrants included in the analysis (corresponding values of retinal thickness are reported inside the grid); (B) Enlarged color-FAF of an healthy eye included as control showing the 9 sites where quantitative analysis of color-FAF parameters (GEFC/REFC intensity and emission wavelength) was performed (indicated by white arrowheads); (C) Color-FAF of a patient with moderate non-proliferative DR and DME showing in the white box at the bottom-right corner of the image a detail of the inner inferior quadrant: the site of analysis (indicated by the white arrowhead) was carefully chosen to select an area where no concomitant lesions (in this case microaneurysms and hemorrhages) were present. FAF: fundus autofluorescence; DM: diabetes mellitus; DR: diabetic retinopathy; ETDRS: early treatment diabetic retinopathy study; GEFC/REFC: green/red emission fluorescence components; DME: diabetic macular edema.