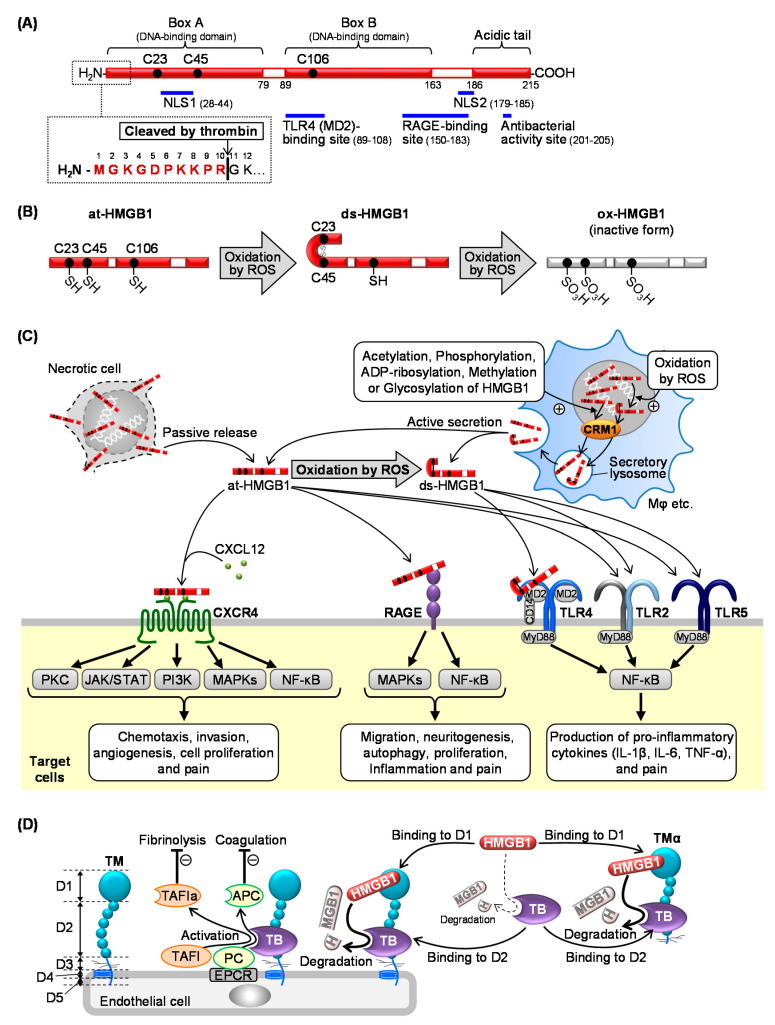
Figure 1.
Structure, origins/targets, and inactivation of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1). (A) The structure and thrombin cleavage site of HMGB1. (B) Redox-dependent structural conformation of HMGB1. (C) Extracellular release and membrane receptors of HMGB1. (D) Thrombin-dependent degradation of HMGB1 by thrombomodulin and thrombomodulin alfa. NLS, nuclear-localization signal; at-HMGB1, all-thiol HMGB1; ds-HMGB1, disulfide HMGB1; ox-HMGB1, fully-oxidized HMGB1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CRM1, chromosome-region maintenance 1; TB, thrombin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CXCR4, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; CXCL12, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; RAGE, receptor for advance glycosylation end products; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TM, thrombomodulin; TMα, thrombomodulin alfa; TAFI, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TAFIa, the activated form of TAFI; PC, protein C; APC, activated protein C; D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5, domain 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 of thrombomodulin; EPCR, endothelial protein C receptor.