Fig. 1.
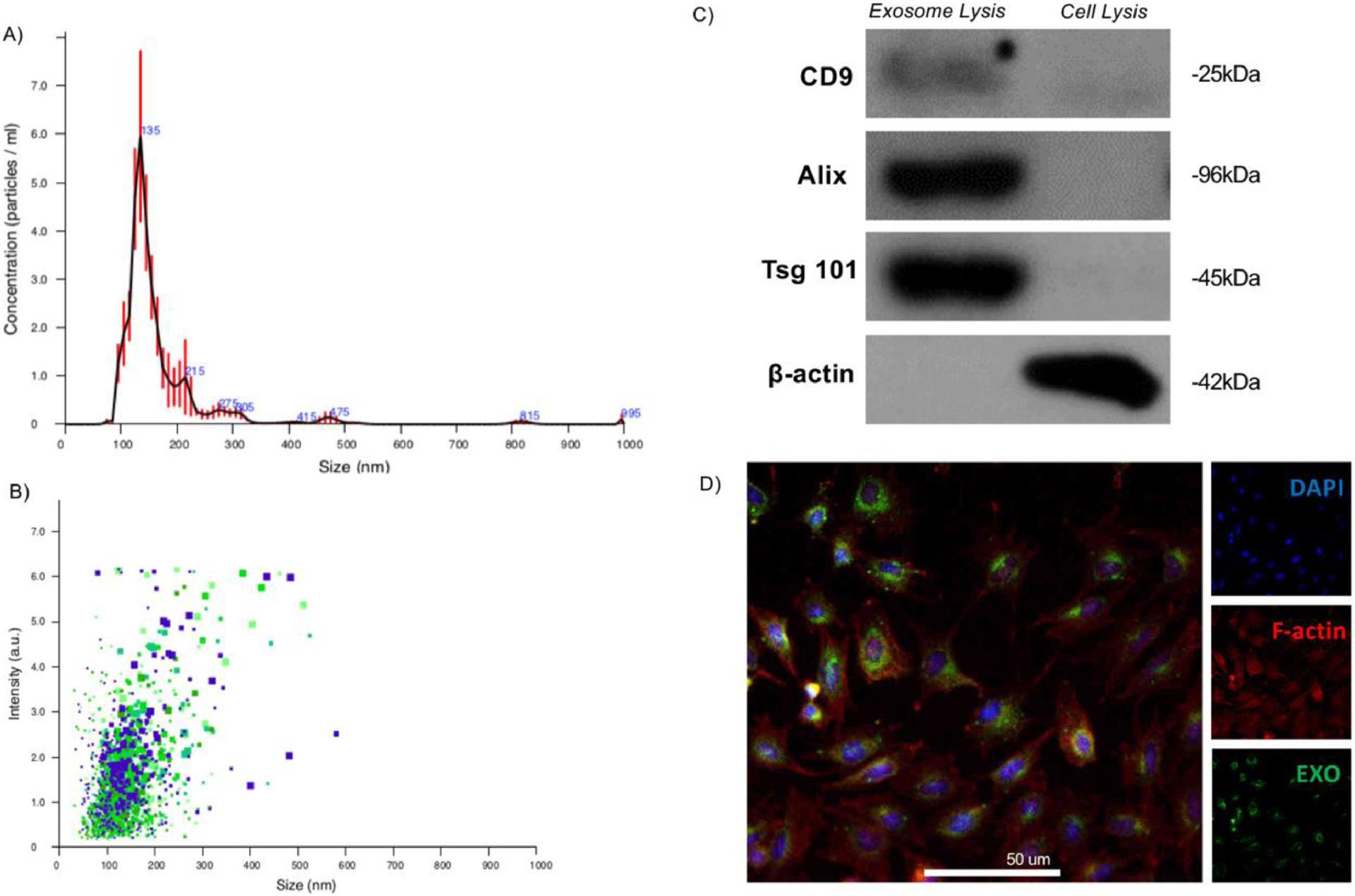
Isolation and characterization of exosomes derived from dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). Exosomes were physically characterized by their size using nanotracking analysis, indicating that freshly isolated exosomes are of the characteristic hydrodynamic diameter (davg = 135 nm, A), and uniformly sized (B). Molecular profiling by Western blot indicates that the isolated exosomes are highly enriched for characteristic exosome surface markers not abundant in the total cell isolate (C). Freshly isolated exosomes were fluorescently labelled, as described, and their uptake by recipient primary mouse bone marrow stromal cells (mBMSCs) after 30 minutes incubation and visualized by confocal microscopy (D; blue: DAPI, red: F-actin, green: membrane-fluorescent exosomes; scale: 50 μm).
