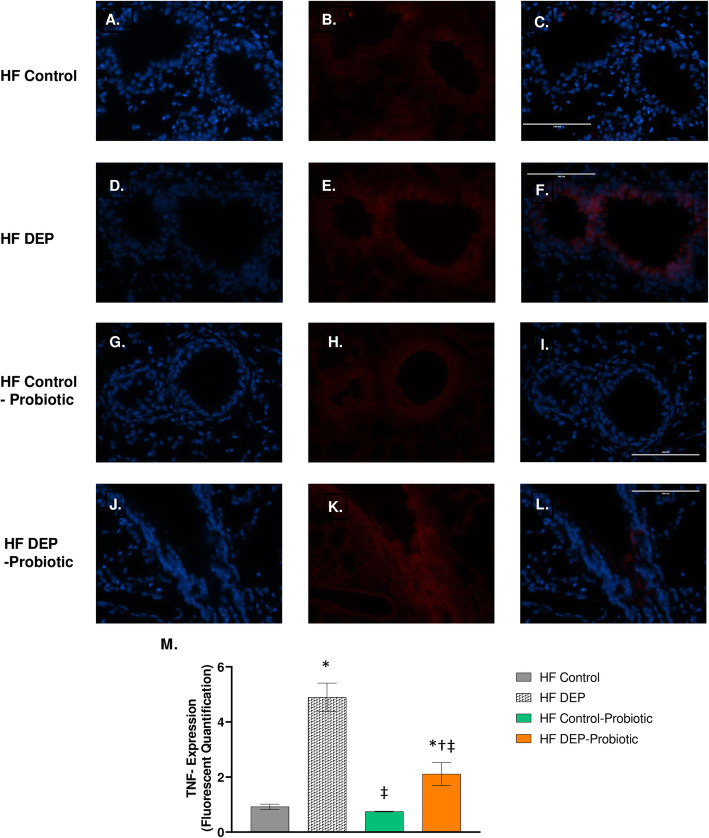
Fig. 13.
Probiotic supplementation attenuates the pro-inflammatory TNF-α response with diesel exhaust particle exposure. Representative images of TNF-α expression in the lungs of C57Bl/6 mice, on a high-fat (HF) diet exposed to either (a–c) saline, (d–f) DEP – 35 μg PM, or (g–i) saline and probiotics - 0.3 g/day (~ 7.5 × 107 cfu/day) and (j-l) DEP and probiotics. Red fluorescence indicates TNF-α expression, blue fluorescence is nuclear staining (Hoechst). Right panels (c, f, i, l) are merged figures of left (blue; a, d, g, j) and center (red; b, e, h, k) panels. m Graph of histology analysis of lung TNF-α fluorescence. 40x magnification, scale bar = 100 μm. Data are depicted as mean ± SEM with *p < 0.05 compared to HF Control, †p < 0.05 compared to HF Control - Probiotics, ‡p < 0.05 compared to HF DEP by two way ANOVA