Figure 5. MYC inhibition prevents entry into S phase and reduces replication associated stress in FA lymphoblastoid cells.
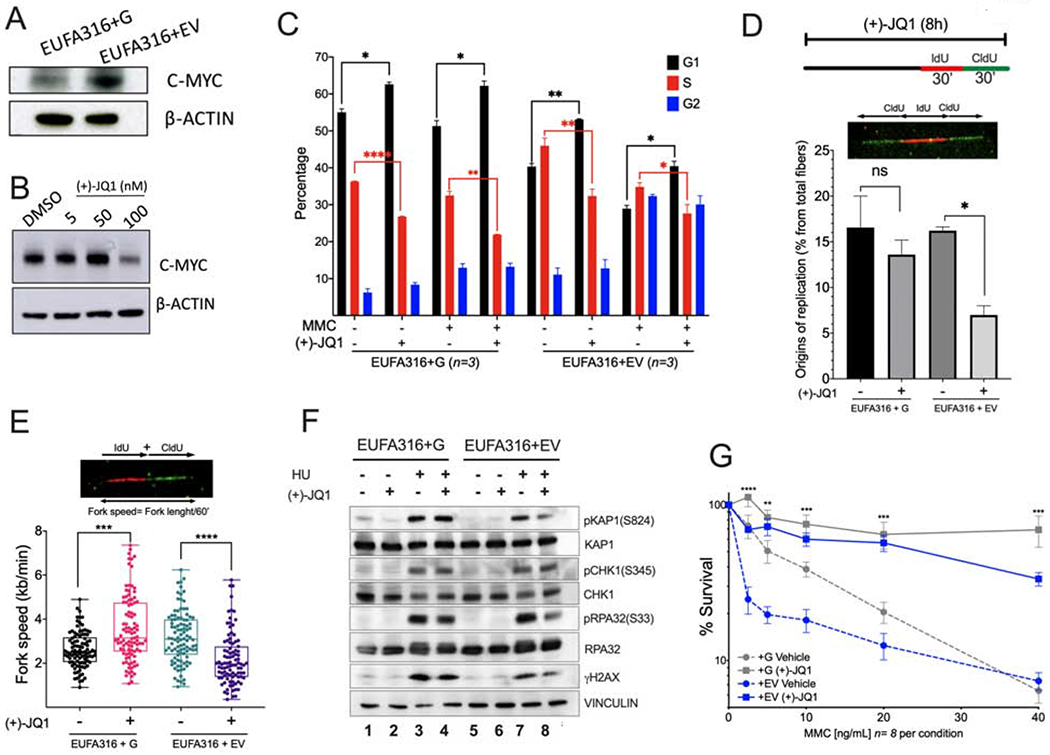
(A) Western blots of the lysates of FANCG-deficient human lymphoblastoid cells (EUFA316+EV) and FANCG-complemented lymphoblastoid cells (EUFA316+G).
(B) Western blots of the lysates of EUFA316+EV cells exposed to the BET bromodomain inhibitor (+)-JQ1 for 48 h.
(C) EUFA316+G and EUFA316+EV cells were treated for 24h with Mitomycin C (MMC) (20 ng/ml) and (+)-JQ1 (50 nM) and cell cycle distribution was analyzed.
(D) (+)-JQ1 reduces the amount of new replication origins in the FANCG-deficient lymphoblastoid cells. EUFA316+G and EUFA316+EV cells were exposed to (+)-JQ1 for 8 h and then incubated with the nucleotide analogs IdU for 30 min followed by CldU for 30 min in presence of (+)-JQ1. DNA fiber assay was carried out and the percentage of fibers with replication origins were quantified per condition.
(E) (+)-JQ1 slows-down replication fork speed in the FANCG-deficient lymphoblastoid cells. EUFA316+G and EUFA316+EV cells were treated as described in panel D. DNA fiber assays were performed and the fiber length composed by IdU tracts plus CldU tracts was measured and divided by the incubation time in the presence of the analogs. At least 100 fibers were analyzed per sample.
(F) Western blots of the lysates of EUFA316+EV and EUFA316+G cells after treatment with hydroxyurea (HU) and (+)-JQ1 for 24 h.
(G) Survival of the FANCG-deficient EUFA316+EV and EUFA316+G cells exposed to increased concentrations of MMC and (+)-JQ1 (50 nM) for 5 days. The experiment was performed three times and the data from a representative experiment are shown.
Data in (C), (D) and (G) are represented as mean ± SEM. Data in (E) are represented as boxplots. p-values of 0.01 to 0.05 were considered significant (*), p-values of 0.001 to 0.01 were considered very significant (**) and p-values of <0.001 were considered extremely significant (***, ****). See also Supplementary Figure 5.
