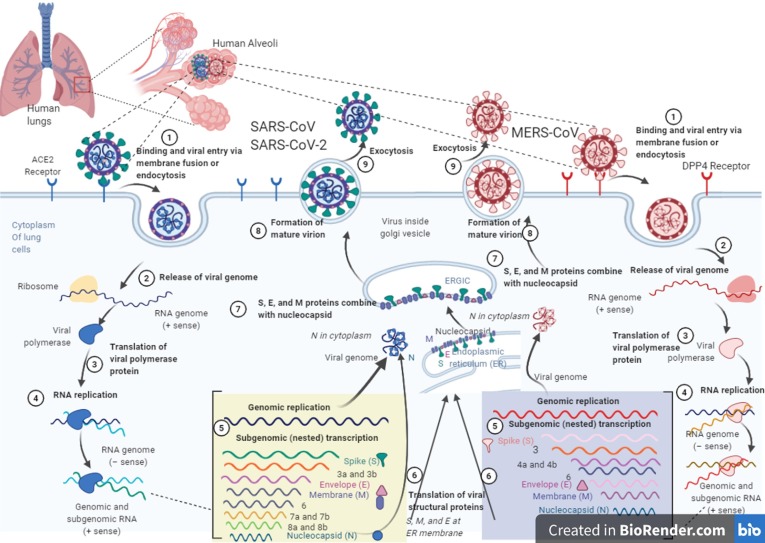
Fig. 2.
The life cycles of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 in host lung cell. The entrance of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV viruses into cells are happened by an endosomal pathway through special receptors on the host cells. The receptor of SARS-CoV is ACE2, which binds through S glycoprotein on the surface of viruses. MERS-CoV bind to the DPP4 receptor through S glycoproteins. The viral RNA is released into the cytoplasm after the virus has entered the host cell. Replication of genome leads to the production of full-length (−) RNA copies of the genome as templates for full-length (+) RNA genomes. Also, transcription of the genome leads to the production of 7–9 RNAs, which produces some structural proteins. S, M, and E proteins are produced at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Nucleocapsids are manufactured in the cytoplasm from genomic RNA and N proteins, followed by budding into the lumen of the intermediate ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum (ER)–Golgi compartment). The virions are then released by exocytosis from the infected host cell. (life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 is similar to SARS-CoV). The artwork is provided by BioRender (https://biorender.com/).