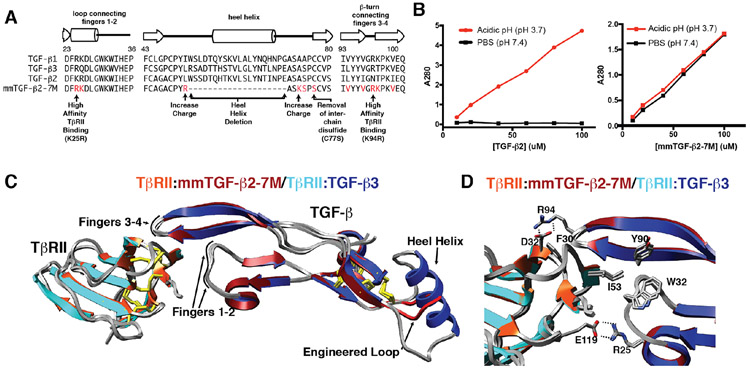
Figure 5.
Engineered TGF-β monomer and characterization of its structure and solubility. A. Design of the engineered TGF-β monomer, known as mmTGF-β2-7M, which is based on the backbone of TGF-β2. mmTGF-β2-7M, in addition to lacking the heel helix and bearing a substitution of Cys77 with Ser, also has two substitutions to increase the charge in the loop that serves to replace the heel helix and seven substitutions in the loops connecting fingers 1-2 and 3-4 that contact TβRII. B. Solubility of TGF-β2 dimers (left panel) and mmTGF-β2-7M (right panel). Solubility was assessed by measuring the absorbance at 280 nm of the supernatant after TGF-β2 or mmTGF-β2-7M are diluted from an acidic stock where they are highly soluble into either acidic solution (pH 3.7) or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at neutral pH (pH 7.4) and centrifuged. C. Overlay of the 1.8 Å crystal structure of mmTGF-β2-7M:TβRII complex (dark red and orange ribbons, respectively) with one of the TGF-β3 monomers and its bound TβRII from the 3.0 Å crystal structure of the TGF-β3:TβRII:TβRI complex (PDB 2PJY, TGF-β3 monomer and TβRII shown in dark blue and cyan ribbon, respectively; TβRI not shown for clarity). Newly created loop in mmTGF-β2 (red) which takes the place of the heel (α3) helix in TGF-β2 is depicted in red. D. Overlay as in panel C, but expanded to show the near identity of critical hydrophobic and hydrogen-bonding/electrostatic interactions shown previously to be essential for high affinity TGF-β3:TβRII binding 40, 42. Figure is adapted and reproduced with permission from Kim, et. al, J. Biol. Chem., 292, 7173-7188 (2017).