Figure 1.
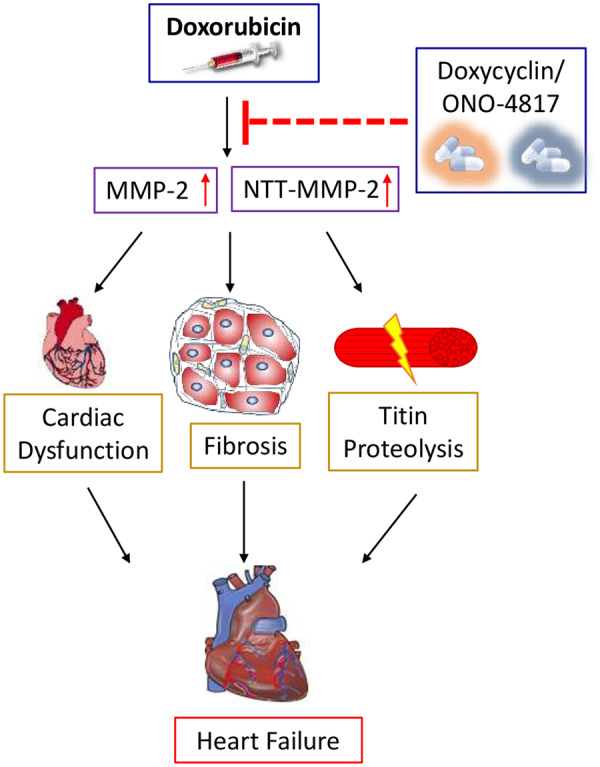
Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity can be attenuated by MMP inhibitors. Doxorubicin (DOX) increases in MMP-2 and NTT-MMP-2 activity, which leads to cardiac dysfunction, fibrosis, titin proteolysis, and eventually heart failure. Inhibition of MMP-2 and NTT-MMP-2 expression with doxycycline or ONO-4817, prevents DOX induced cardiac toxicity and heart failure.
