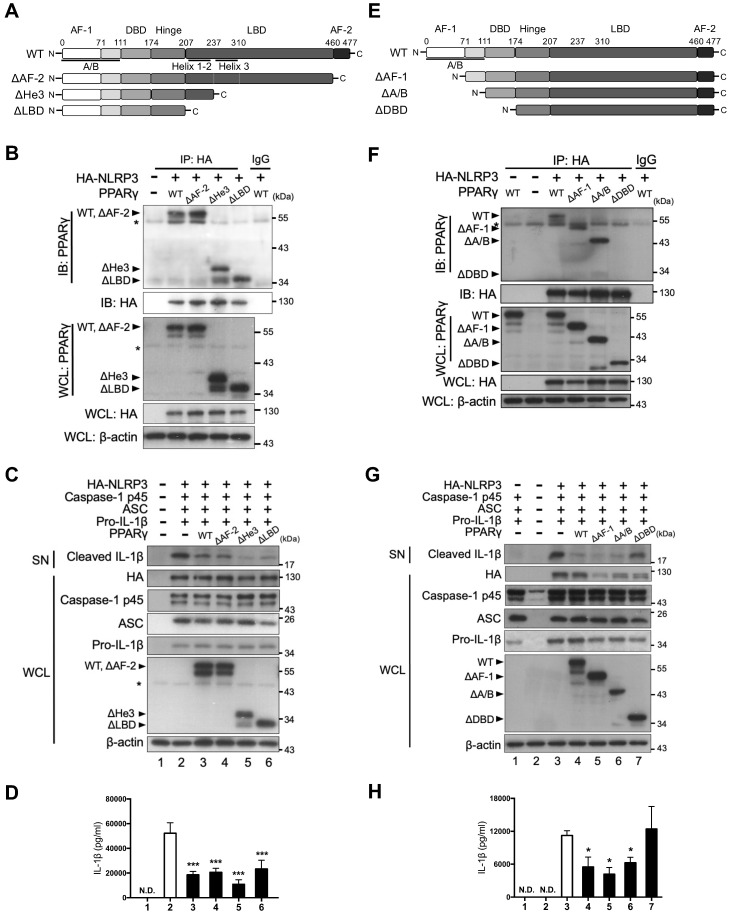
Figure 4.
PPARγ DBD mediated the interaction with NLRP3 and the inhibitory effect on NLRP3 inflammasome activation. (A) Schematic diagrams show PPARγ LBD-truncated mutants (ΔAF-2, ΔHe3, and ΔLBD). (B) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis of the interaction between LBD-truncated PPARγ and HA-tagged NLRP3 in HEK293T cells. (C) Immunoblot analysis of mature IL-1β in the supernatant (SN) and NLRP3 inflammasome components in whole cell lysate (WCL) of NLRP3 inflammasome-reconstituted HEK293T cells overexpressing LBD-truncated PPARγ. (D) IL-1β levels detected by ELISA from three independent experiments. (E) Schematic diagrams show PPARγ N-terminal truncated mutants (ΔAF-1, ΔA/B, and ΔDBD). (F) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis of the interaction between N-terminal truncated PPARγ and HA-tagged NLRP3 in HEK293T cells. (G) Immunoblot analysis of mature IL-1β in the SN and NLRP3 inflammasome components in WCL of NLRP3 inflammasome-reconstituted HEK293T cells overexpressing N-terminal truncated PPARγ. (H) IL-1β levels detected by ELISA from three independent experiments. AF-2, activation function 2; He3, helix-3; LBD, Ligand binding domain; AF-1, activation function 1; DBD, DNA binding domain. PPARγ band is labeled with arrowhead and a non-specific band is labeled with asterisk. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Fisher's LSD test. Representative blots are from three independent experiments. Experiment replicates are shown in Figure S13.