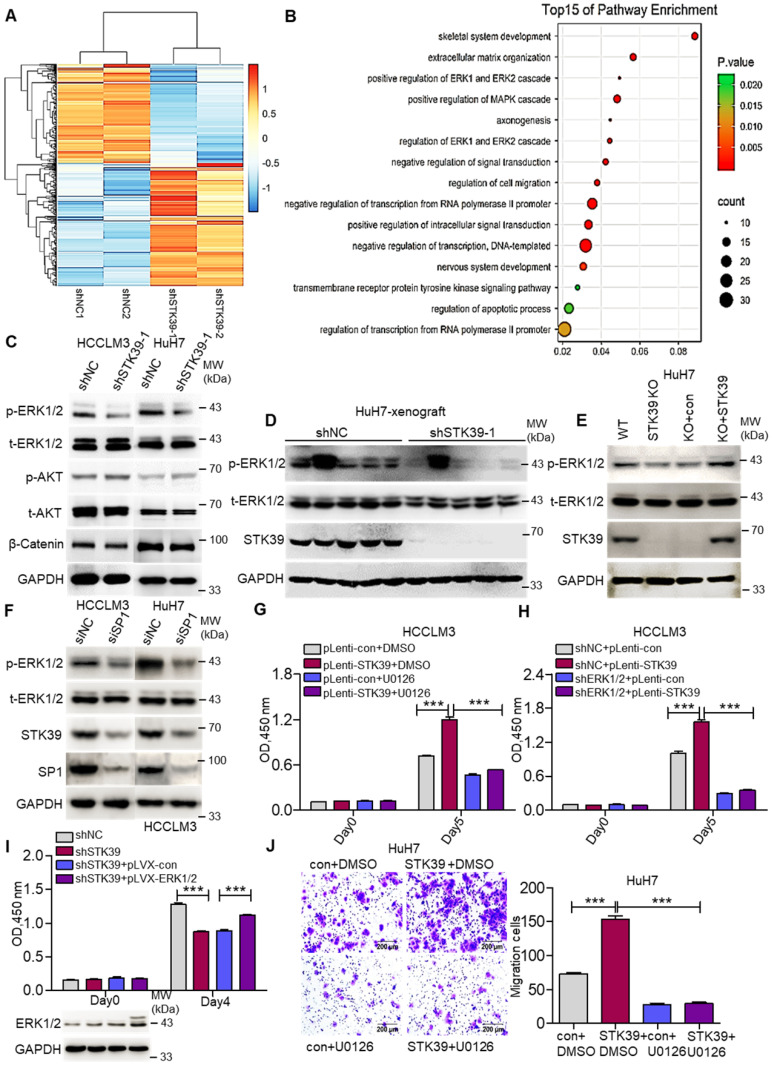
Figure 5.
STK39 mediates oncogenic effects on HCC cells through activating the ERK1/2 pathway. (A) Stable knockdown of STK39 in HuH7 cells by shRNA, the differentially expressed genes were identified by RNA-sequence analysis. (B) Pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in RNA-sequence data from (A). (C) Stable knockdown of STK39 in HCC cells by shRNA, the levels of p-ERK1/2, p-AKT and β-catenin were examined by immunoblotting. (D) Immunoblotting analysis of p-ERK1/2 level in tumor xenografts generated from subcutaneous inoculation of STK39 stable knockdown cells in mice. (E) STK39-/- HuH7 cells were reconstituted by infection of STK39 overexpression lentivirus, the levels of p-ERK1/2 and STK39 were assessed by immunoblotting. (F) HCC cells were transfected with negative control siRNA or SP1-specific siRNA for 72 h to knockdown SP1, the levels of p-ERK1/2, STK39 and SP1 were examined by immunoblotting. (G) STK39-overexpression and control HCCLM3 cells were treated with or without U0126, and the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (H) ERK1/2-knockdown and control HCCLM3 were infected with control or STK39 overexpression lentivirus, the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (I) Stable overexpression of ERK1/2 in STK39-knockdown HCCLM3 cells, the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (J) STK39-overexpression and control HuH7 cells were treated with or without U0126, migrated cells were measured by transwell assay. Data are shown as mean ±SEM. ***p<0.001.