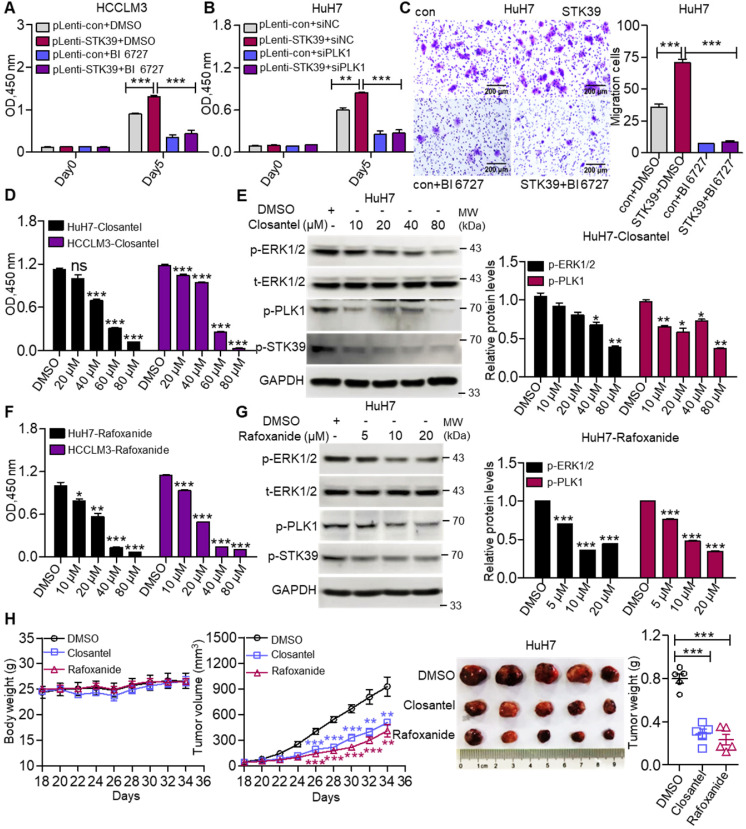
Figure 7.
STK39 promotes the progression of HCC via activating the PLK1-ERK1/2 pathway. (A) STK39-overexpression and control HCCLM3 cells were treated with or without BI 6727, and the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (B) STK39-overexpression and control HuH7 cells were transfected with negative control siRNA or PLK1-specific siRNA for 48 h, the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (C) STK39-overexpression and control HuH7 cells were treated with or without BI 6727, migrated cells were measured by transwell assay. (D) HCC cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Closantel for four days, the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (E) HuH7 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Closantel for 2 h, the levels of p-ERK1/2, p-PLK1 and p-STK39 were examined by immunoblotting. (F) HCC cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Rafoxanide for four days, the viability of cells was measured by CCK8 assay. (G) HuH7 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Rafoxanide for 2 h; the levels of p-ERK1/2, p-PLK1 and p-STK39 were examined by immunoblotting. (H) HuH7 cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice (n=5/group), after 18 days, mice were treated with or without 20 mg/kg STK39 inhibitors every two days for 16 days (Tumor sizes and the weights of mice were measured every two days). After 34 days, the mice were euthanized, and the tumor weights were measured. Data are shown as mean ±SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant.