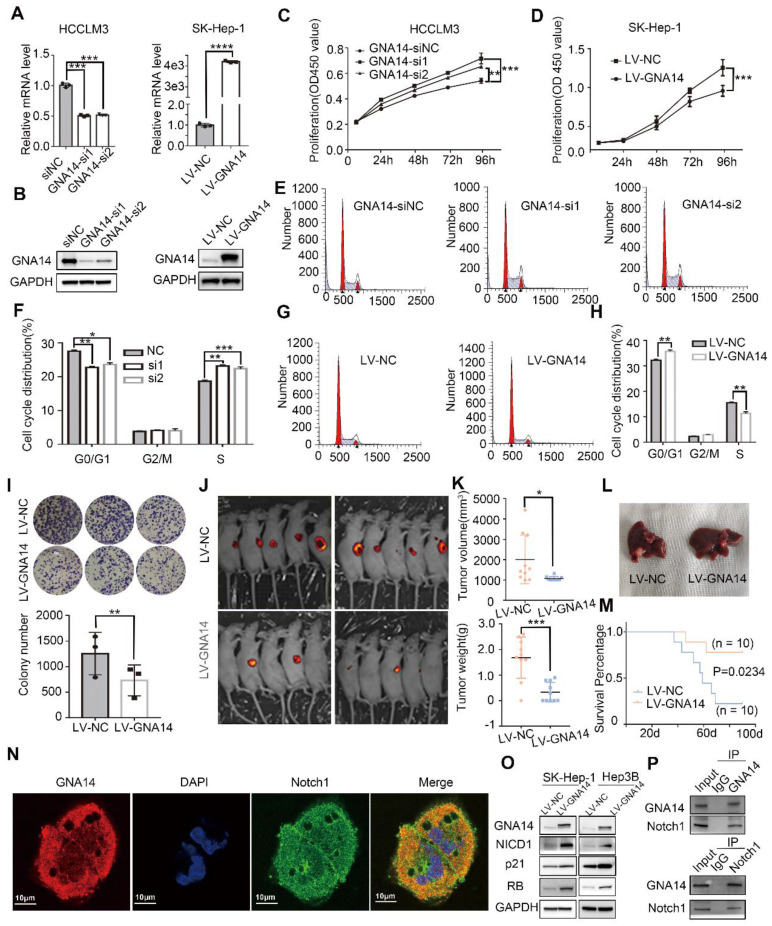
Figure 5.
GNA14 suppresses the proliferation of HCC by promoting Notch1 cleavage. (A) qRT-PCR was performed to verify the effect of GNA14 knockdown and overexpression. (B) Western blot was performed to verify the effect of GNA14 knockdown in HCCLM3 cells and overexpression in SK-Hep-1 cells. (C) CCK8 assay was performed to determine the proliferation of HCCLM3 cells infected with GNA14 siRNA or si-negative control (si-NC). (D) CCK8 assay was performed to determine the proliferation of SK-Hep-1 cells infected with GNA14 lentivirus (LV-GNA14) or lentivirus negative control (LV-NC). (E, F) Effects of GNA14 knockdown on the cell cycle distribution of HCCLM3 cells. (G, H) Effects of GNA14 overexpression on the cell cycle distribution of SK-Hep-1 cells. (I) Colony assay with cells with LV-GNA14 or LV-NC. (J) Fluorescent image of subcutaneous human HCC xenograft model with GNA14 stably overexpressed cells or control cells. (K) Tumor volume and weight of HCC xenograft were measured. (L) Orthotopic liver tumor model in nude mice with GNA14 stably overexpressed cells or control cells. (M) The survival of orthotopic tumor model mice was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. (N) Immunofluorescence analysis of cytoplasmic distribution of GNA14 and Notch1 in SK-Hep-1 cells. (O) The expression level of NICD1, RB, and P21 in GNA14 overexpressed SK-Hep-1 and Hep3B cells was examined by western blot. (P) Lysates of SK-Hep-1 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-GNA14 or anti-Notch antibody, and were examined using western blot analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to analyze the survival percentage.