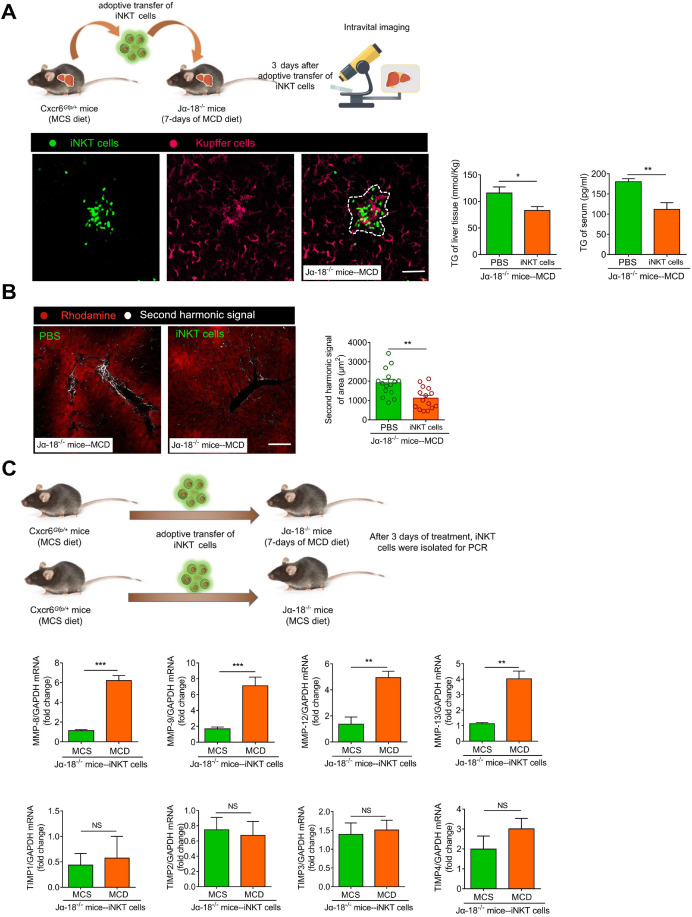
Figure 8.
Adoptive transfer of iNKT cells improves lipid accumulation and inhibits fibrosis in Jα18-/-mice. (A) Left: Experimental model of adoptive transfer iNKT cells. Representative images were obtained from ≥ 3 experiments to examine the interactions between iNKT cells (green) and Kupffer cells (fuchsia, F4/80 antibody-labeled Kupffer cells) in Ja18-/-mice adoptively transferred with iNKT cells. Scale bar, 100 µm. Right: Quantitative analysis of intrahepatic TG concentrations and serum TG levels in Ja18-/-mice (n = 5) adoptively transferred with iNKT cells or PBS. (B) Left: Representative images were obtained from ≥ 3 experiments to examine the second harmonic signal (white) in Ja18-/-mice adoptively transferred with iNKT cells or PBS, liver leaflet outline visualized by Rhodamine (red) markers. Scale bar, 100 µm. Right: Quantitative analysis of second harmonic signal of area in Ja18-/-mice (n = 5) adoptively transferred with iNKT cells or PBS. (C) Experimental model of adoptive transfer iNKT cells. Quantitative mRNA level analysis of MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-12, MMP-13, TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 from iNKT cells adoptively transferred into MCS or MCD fed Ja18-/-mice (n = 5). Data represent mean relative expression ±SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 using two-tailed unpaired student's t-test.