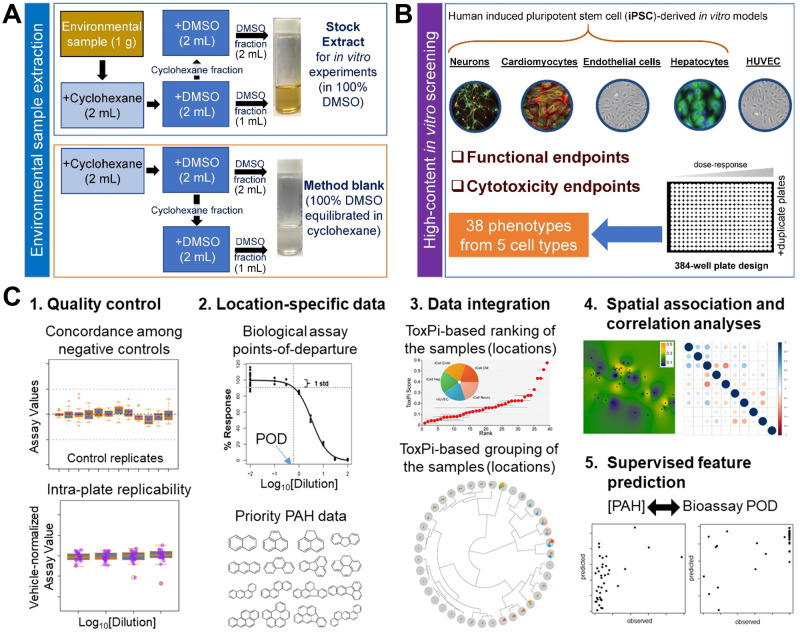
Figure 2.
Overall experimental design of the study. A, A schematic diagram of the extraction procedure for environmental soil samples. B, Bioactivity data collection overview. In vitro experiments were performed in 384-well plates using 5 human cell types. C, Data analysis workflow. Quality control (QC) was used to filter assay/cell line combinations to ensure high concordance among controls and high intra- and inter-plate reproducibility. For the assays passing QC, points of departure (POD) were estimated using logistic (Hill) function curve fitting, and overall and cell-type-specific measures of bioactivity computed across the assays. Analysis of bioactivity was further grounded in comparisons to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) data on the same samples. Data were integrated using ToxPi approach. Spatial association and correlations between biological and PAH data were evaluated. Finally, trained (supervised) models to “predict” the PAH data from bioactivity or vice versa were constructed.