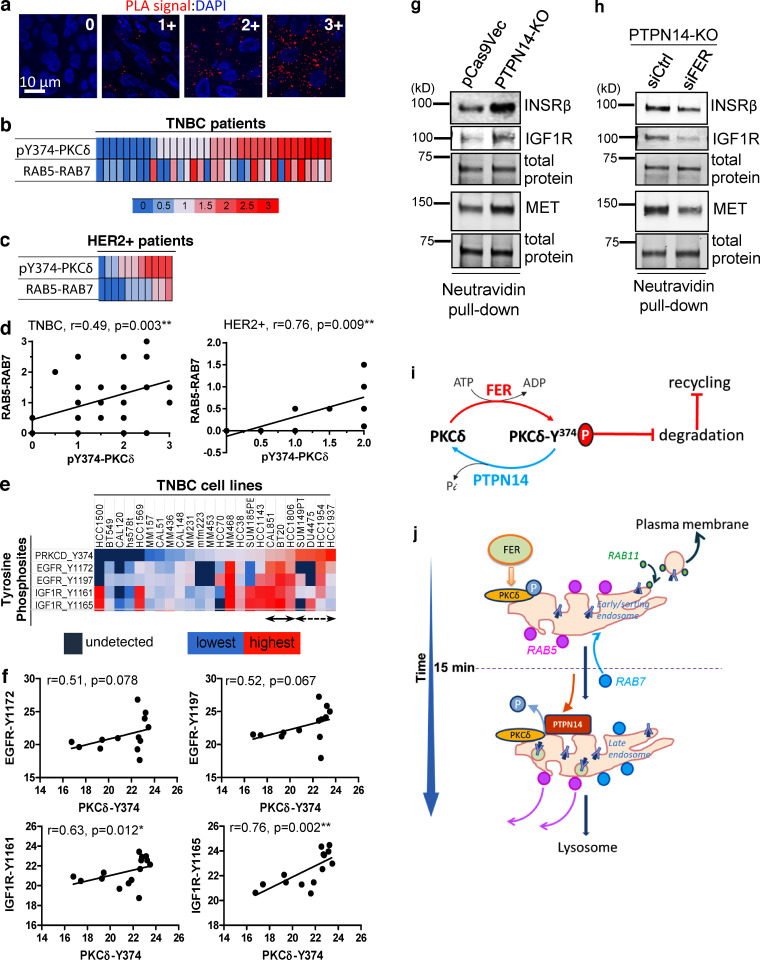
Figure 10.
High pY374-PKCδ is associated with dysregulated RTK trafficking and increased signaling in breast cancer. (a–d) Increased pY374-PKCδ is correlated with increased RAB5-RAB7 colocalization in TNBC and HER2+ breast cancers. A TMA of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples from n = 35 TNBC patients and n = 11 HER2+ breast cancer patients (two cores per patient) were stained for pY374-PKCδ (using rabbit anti-pY374-PKCδ and mouse anti-PKCδ Abs) or RAB5-RAB7 colocalization (using rabbit anti-RAB5 and mouse anti-RAB7 Abs) by PLA (red dots) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Data show representative confocal images of PLA signal strengths on a scale of 0–3+ (a) and heatmaps of pY374-PKCδ signals (upper panels) and RAB5-RAB7 colocalization signals (lower panels) in triple-negative (b) and HER2+ (c) breast cancers. Correlation between pY374-PKCδ levels and RAB5-RAB7 colocalization levels (d) in TNBC (left) and HER2+ breast cancer (right) were analyzed by Spearman linear regression analysis. (e and f) Elevated pY374-PKCδ correlates with RTK activation in TNBC cell lines. Phosphorylation levels of Y374-PKCδ, Y1172-EGFR, Y1197-EGFR, Y1161-IGF1R, and Y1165-IGF1R were quantified by phosphoproteomics from 24 TNBC lines and presented as a heatmap (e) or as a correlation between pY374-PKCδ expression and pY1172-EGFR, pY1197-EGFR, pY1161-IGF1R, and pY1165-IGF1R (f), using Spearman linear regression analysis. (g and h) pY374-PKCδ–induced cell surface RTK expression is dependent on FER. Western blots of cell surface biotinylated proteins from control (pCas9Vec) or PTPN14-KO cells (g) or from PTPN14-KO cells transfected with control (siCtrl) or FER siRNAs (siFER; h), pulled down using NeutrAvidin Sepharose and probed with the indicated antibodies. Data showing representative blots from n = 3 biological replicates. (i) Proposed model for the FER-PKCδ-PTPN14 axis in regulating RTK recycling and degradation. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Y374-PKCδ by FER and PTPN14, respectively, regulates degradation and recycling. (j) Proposed model of recruitment of pY374-PKCδ, PTPN14, RAB5, RAB11, and RAB7 to the endosomes. Upon ligand binding, Y374-PKCδ is phosphorylated by FER and recruited to early endosomes containing RAB5. PTPN14 is recruited later, which coincides roughly with RAB7 recruitment, causing dephosphorylation of pY374-PKCδ, which facilitates RAB5 shedding from the transient RAB5-RAB7–positive transitional endosome to enable its maturation into late endosome and fusion with lysosome leading to degradation of RTK cargo.