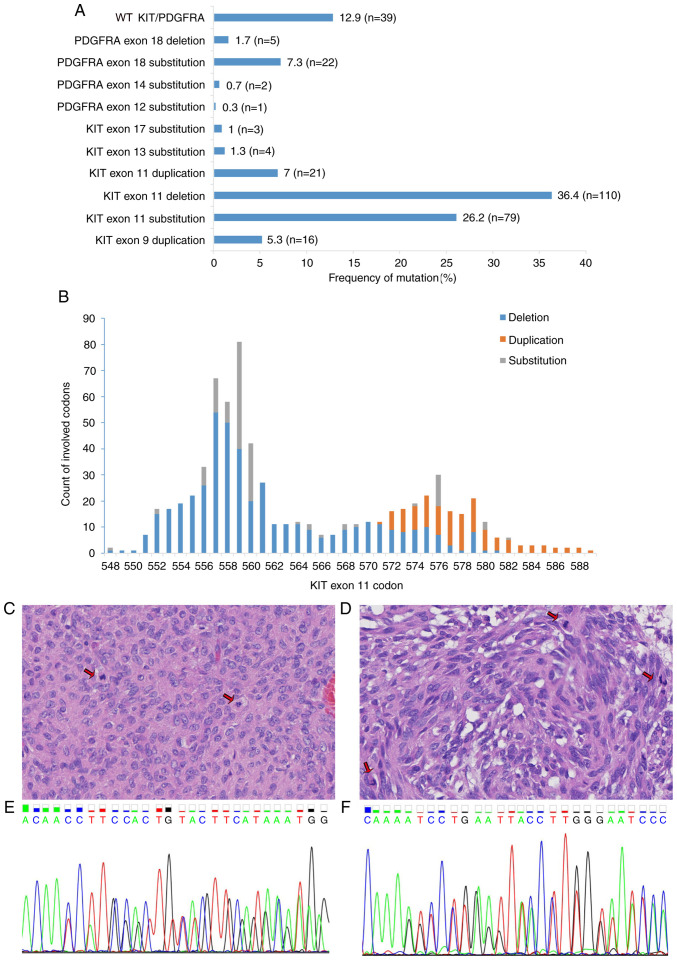
Figure 1.
Spectrum of KIT and PDGFRA mutations in 302 cases of GISTs. (A) Distribution of KIT and PDGFRA mutations. KIT exon 11 deletion was the most common genotype (36.4%, n=110) among the GISTs. Less frequent mutations included KIT exon 11 substitution (26.2%, n=79) and PDGFRA exon 18 substitution (7.3%, n=22). KIT exon 17 substitution, PDGFRA exon 12 substitution and exon 14 substitution were rare genotypes. (B) Counts of KIT exon 11 codons affected by deletion, duplication and substitution are depicted. Deletions and substitutions frequently involved codons 557–560, whereas duplication was observed in codons 572–580. (C-F) One patient with a GIST exhibited the coexistence of KIT exon 11 deletion and exon 13 duplication. The specimen of this patient presented (C) epithelioid and (D) spindle morphology and high mitotic activity (arrows). Hematoxylin and eosin staining (magnification, ×400). In this patient, the (E) in-frame deletion of KIT exon 11 (codons 553–558) and (F) in-frame insertion of exon 13 (one base pair insertion between codons 642 and 643) were detected. KIT, KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; PDGFRA, platelet derived growth factor receptor α; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor.