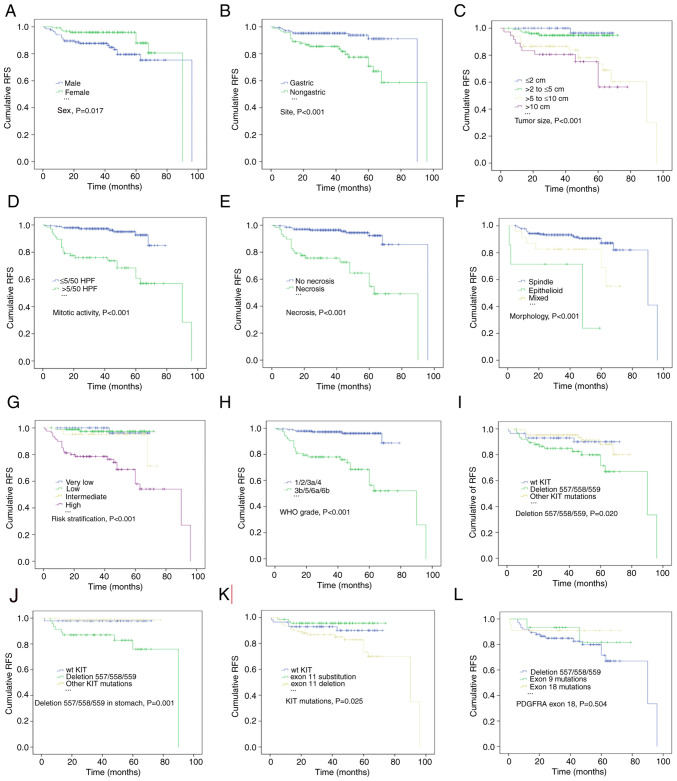
Figure 4.
Estimates of RFS in patients with GISTs by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with log-rank tests. (A) Male sex, (B) non-gastric origin, (C) tumor size >5 cm, (D) mitotic count >5/50 HPF and (E) necrosis were associated with a lower RFS rate. (F) Compared with spindle and mixed morphology, the epithelioid subtype was significantly associated with a shorter RFS. According to the (G) National Institutes of Health and (H) WHO classifications, patients classified as high risk and high grade (3b/5/6a/6b) had significantly lower RFS rates. KIT deletions involving codons 557/558/559 significantly reduced the RFS rates of patients with (I) GISTs and (J) gastric GISTs compared with those of patients with other KIT mutations or WT KIT. (K) KIT exon 11 substitution indicated a significantly improved RFS for patients with GISTs. (L) Patients with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations had a higher RFS rate, although the difference from that of patients with other PDGFRA mutations was not statistically significant. RFS, relapse-free survival; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; HPF, high-power fields; WHO, World Health Organization; KIT, KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; WT, wild-type; PDGFRA, platelet derived growth factor receptor α.