Extended Data Figure 6 |. Arf79F knockdown kills transformed and normal stem cells through necrosis.
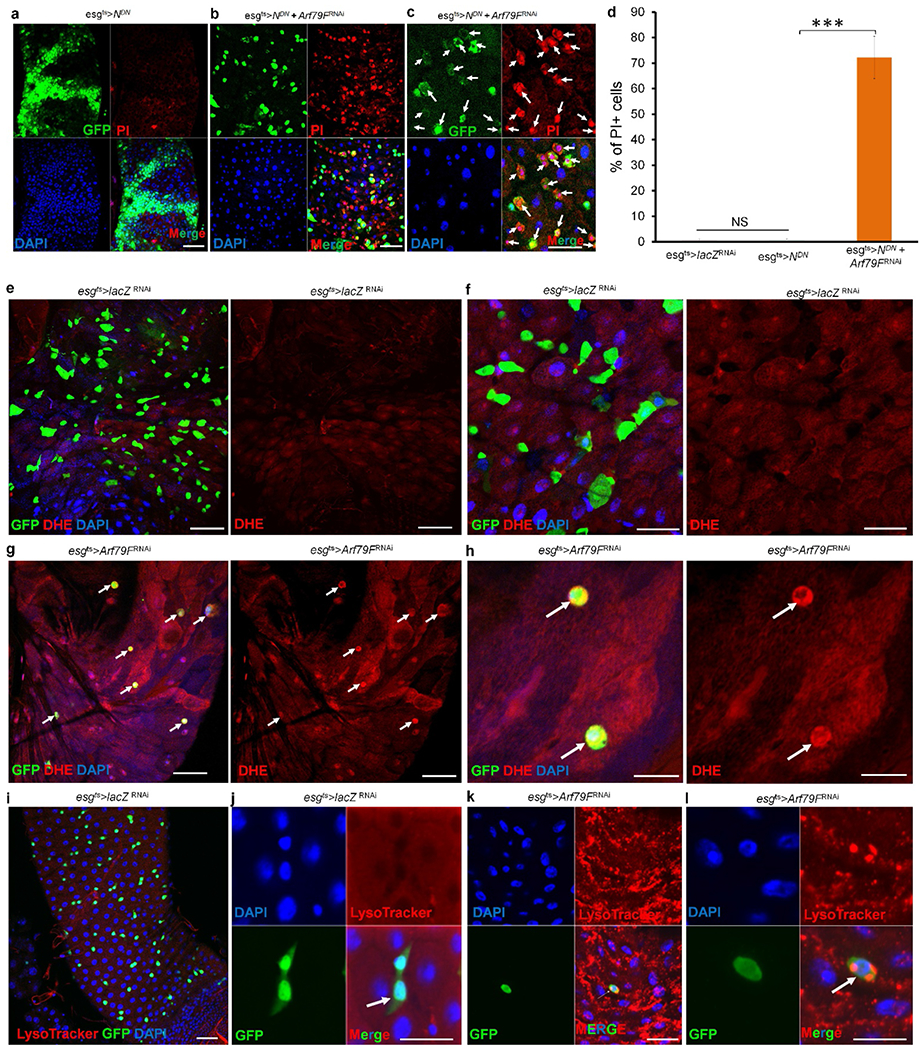
(a–d) The genotypes of the flies in each panel were: a, esgts > NDN, 29 °C, 4 d (n = 25). b, c, esgts > NDN + Arf79FRNAi, 29°C, 4 d (n = 25). d, Quantification of PI+ cells in the indicated panels. Data show the mean ± s.d. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.0001. NS, not significant (P > 0.05). White arrows point to GFP- and propidiumiodide-positive stem cells in c. e–l, The genotypes of the flies in each panel were: e, f, i, j, esgts > lacZRNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (e, f, n = 27; i, j, n = 30). g, h, k, l, esgts > Arf79FRNAi, 29 °C,7 d (g, h, n = 45; k, l, n = 30). White arrows point to GFP+ stem cells. No DHE or LysoTracker signals were detected in the wild-type midgut, but these signals were intense in the esgts > Arf79FRNAi flies, indicating that the dying ISCs had accumulated ROS and were intracellularly acidified. The posterior midguts of flies with the indicated genotypes were dissected, stained with the indicated antibodies or dyes and analysed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars in a–c and e–l: 10 μm.
