Figure 2 |. The COPI–Arf79F complex regulates stem cell survival through a lipolysis pathway.
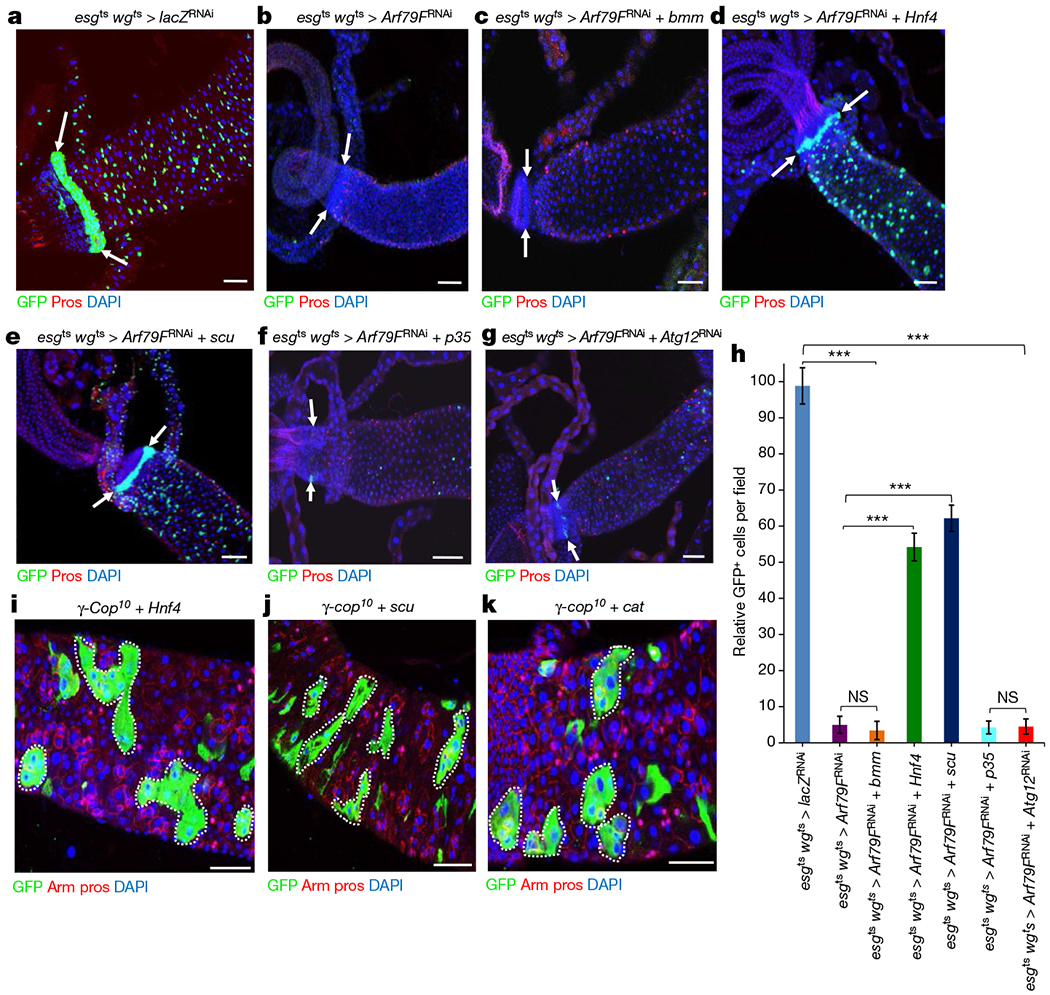
a–g, Representative images are shown. The genotypes of the flies in each panel were: a, esgts wgts > lacZRNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 34). b, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 38). c, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi + bmm, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 31). d, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi + Hnf4, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 29). e, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi + scu, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 32). f, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi + p35, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 37). g, esgts wgts > Arf79FRNAi + Atg12RNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 32). h, Quantification of GFP+ cells from midguts isolated from flies with the indicated genotypes. Data are represented as mean ± s.d. Statistical significance determined by Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.0001. NS, not significant (P > 0.05). i–k, MARCM clones of flies with the following genotypes: i, UAS–Hnf4; FRT82B–γ-Cop10, 7 d (n = 30) after clonal induction (ACI). j, UAS-scu; FRT82B-γ-Cop10, 7 d ACI (n = 32). k, UAS–cat; FRT82B–γ-Cop10, 7 d ACI (n = 35). The posterior midguts of flies with the indicated genotypes were dissected, stained with the GFP, Prospero (Pros) and Armadillo (Arm) antibodies and analysed by confocal microscopy. White arrows in a–g point to the hindgut-midgut junction. White dotted lines in i–k outline GFP+ clones. Scale bars in a–g and i–k, 10 μm.
