Extended Data Figure 4 |. The lipolysis-β-oxidation pathway regulates survival of transformed stem cells.
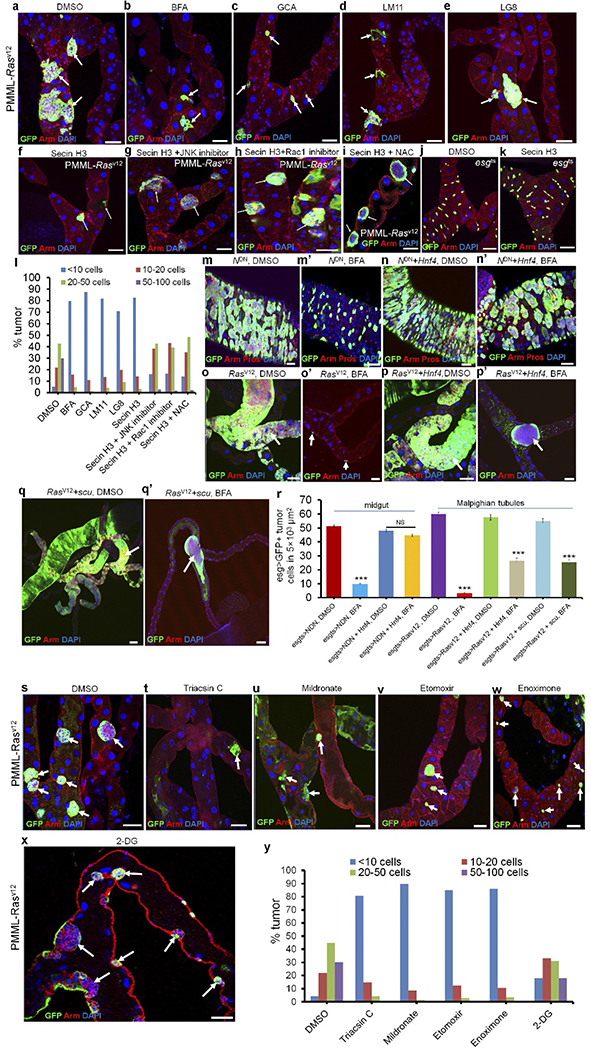
a–l, Arft inhibitors kill RasV12-transformed RNSCs through the ROS–Rac–JNK pathway. The GFP-labelled RNSC tumour clusters were induced by expressing RasV12 in RNSC clones, using the positively marked mosaic lineage (PMML) labelling technique10,50 in adult Drosophila. The flies with RasV12-PMML clones were cultured for 4 d at room temperature on normal food to let the tumour grow and then switched to food with indicated drugs for another 4 d. Flies with RasV12-tumours were given normal food with DMSO (a), 50 ng ml−1 BFA (b), 5 μM GCA (c), 50 μM LM11 (d), 100 μM LG8 (e), 50 μM secin H3 (f), 50 μM secin H3 + 50 μM JNK inhibitor Sp600125 (g), 50 μM secin H3 + 100 μM Rac1 inhibitor (h) or 50 μM secin H3 + 10 mM NAC (i). j,k, esgts flies were fed with normal food with either DMSO (j, n = 20) or 50 μM secin H3 (k, n = 22). n = number of tissues observed. l, Quantification analysis of tumour sizes in Malpighian tubules of indicated panels. We classified all tumours into four categories based on the total number of GFP+ cells in each tumour clone (<10 cells, 10–20 cells, 20–50 cells and 50–100 cells). Total number of tumours investigated for each treatment: DMSO (466 tumours, n = 27 Malpighian tubules), BFA (63 tumours, n = 30 Malpighian tubules), GCA (73 tumours, n = 32 Malpighian tubules), LM11 (94 tumours, n = 35 Malpighian tubules), LG8 (86 tumours, n = 27 Malpighian tubules), secin H3 (64 tumours, n = 25 Malpighian tubules), secin H3 + JNK inhibitor (220 tumours, n = 30 Malpighian tubules), Secin H3 + Rac1 inhibitor (211 tumours, n = 27 Malpighian tubules), and Secin H3 + NAC (297 tumours, n = 35 Malpighian tubules). Arrows point to GFP+ RNSC tumour clusters in a–i. m–r, The lipolysis pathway regulates survival of transformed stem cells. The genotypes of the flies in each panel were: m, m′, esgts > NDN, 29 °C, 4 d (m, n = 30; m′, n = 35). n, n′, esgts > NDN + Hnf4, 29 °C, 4 d (n, n = 25; n′, n = 27). o, o ′, esgts > RasV12, 29 °C, 4 d (o, n = 25; o′, n = 32). p, p′, esgts > RasV12 + Hnf4, 29 °C, 4 d (p, n = 25; p′, n = 32). q, q′, esgts > RasV12 + scu, 29 °C, 4 d (q, n = 23; q′, n = 30). The flies were fed with normal food with either DMSO (m–q) or BFA (m′ and n′, 200 ng ml−1; o′–q′, 50 ng ml−1) for 4 d. Expressing Hnf4 or scu partially blocked the effect of BFA on transformed stem cells. r, Quantification of esg > GFP+ tumour cells in 5 × 103 μm2 per treatment in indicated panels. Data show the mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.0001. NS, not significant (P > 0.05). Arrows point to GFP+ RNSC tumour clusters in o–q′. s–y, FAO inhibitors, but not 2-DG, kill RasV12-transformed RNSCs. The GFP-labelled RNSC tumour clusters were induced by expressing RasV12 in RNSC clones using the PMML technique in adult Drosophila. The flies with RasV12-PMML clones were cultured for 4 d at room temperature on normal food to let the tumour grow and then switched to food with indicated drugs for another 4 d. Flies with RasV12-tumours were given normal food with DMSO (s), 5 μM triacsin C (t), 100 μM mildronate (u, n = 27), 100 μM etomoxir (v), 100 μM enoximone (w, n = 37) or 50 mM 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) (x, n = 32). y, Quantification analysis of tumour sizes in Malpighian tubules of indicated panels. Total number of tumours investigated for each treatment: DMSO (474 tumours, n = 30 Malpighian tubules), triacsin C (47 tumours, n = 32 Malpighian tubules), mildronate (69 tumours, n = 27 Malpighian tubules), etomoxir (73 tumours, n = 35 Malpighian tubules), enoximone (86 tumours, n = 27 Malpighian tubules) and 2-DG (264 tumours, n = 32 Malpighian tubules). Arrows point to GFP+ RNSC tumour clusters. The gut of flies with the indicated genotypes was dissected after cultured, stained with the indicated antibodies and analysed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars in a–k, m–q’ and s–x, 10 μm.
