Extended Data Figure 5 |. Knockdown of components of the COPI–Arf79F–Acsl pathway kill normal and transformed stem cells through necrosis.
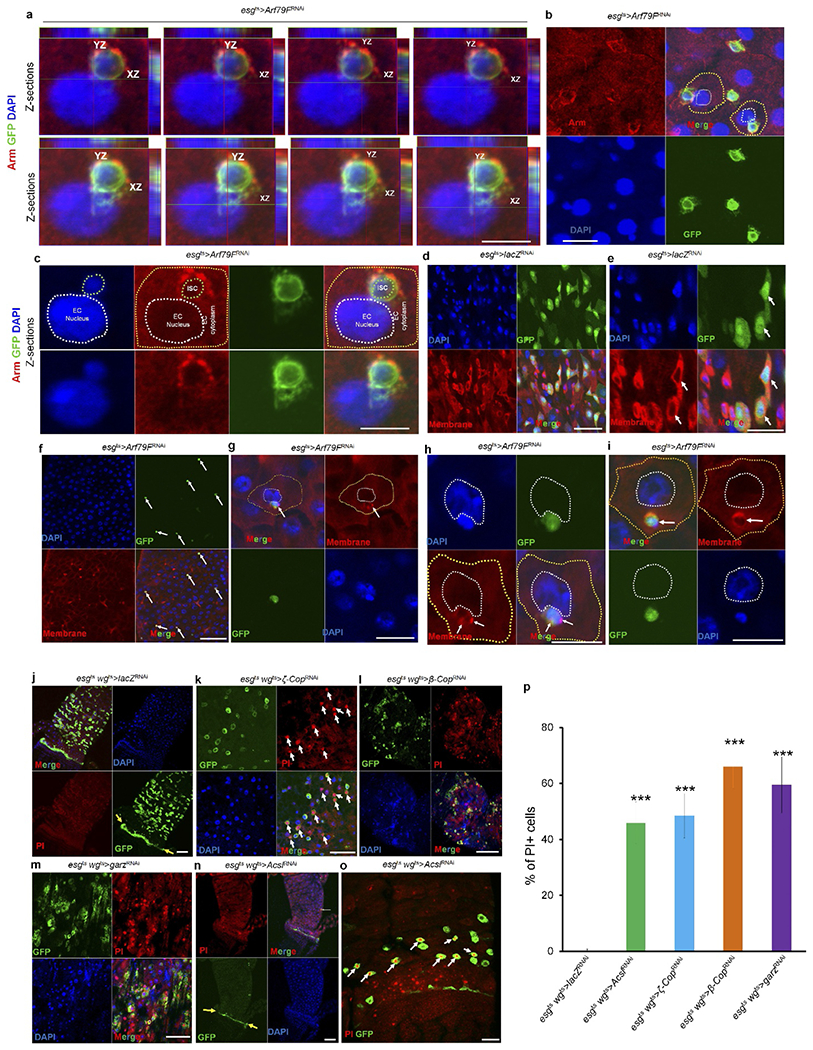
a–i, The genotypes of the flies in each panel were: a–c and f–i, esgts > Arf79FRNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 27). d, e, esgts > lacZRNAi, 29 °C, 7 d (n = 20). In d–i, a dye (CellMask) marks plasma membranes. In a-c and g-i, a dying ISC is engulfed by a neighbouring enterocytes. j, esgts wgts > lacZRNAi, 29 °C, 4 d (n = 30). k, esgts wgts > ζ-copRNAi, 29 °C, 4 d (n = 36). l, esgts wgts > β-CopRNAi > 29 °C, 4 d (n = 34). m, esgts wgts > garzRNAi, 29 °C, 4 d (n = 32). n, o, esgts wgts > AcslRNAi, 29 °C, 4 d (n = 32). p, Quantification of propidium-iodide-positive cells in the indicated panels. Data show the mean ± s.d. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.0001 (compared to control). Yellow arrows point to hindgut–midgut junctions in j and n, white arrows point to GFP- and propidium-iodide-positive stem cells in k and o. The posterior midguts of flies with the indicated genotypes were dissected, stained with the indicated antibodies or reagents and analysed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars in a–o: 10 μm.
