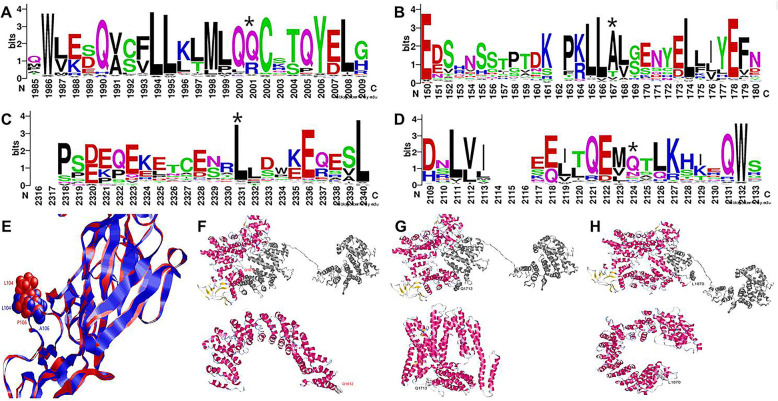
Fig. 2.
Evolutionary and structural modeling analysis of 4 SPG11 mutants. a In patient 1, the mutation site (Q1612X) was located at the 2001amino acid position, and Glutamine was the most conserved. b In patient 2, the mutation site (A106P). was located at the 167amino acid position, Alanine was the most conserved residue, while Proline mutation was not presented in the evolution. c In patient 3, the mutation site (L1870X) was located at the 2331 amino acid position, where Leucine was highly conserved. d In patient 4, the mutation site (Q1713X) was located at the 2124amino acid position and Glutamine was the most conserved. e Structural modeling analysis showed that the mutation of A106P in patient 2 caused a sufficient surface exposure and orientation change of L104, and made the nearby peptide SRNSSTPTEKPKL (92–104) to be a potential epitope. Structural modeling analysis showed that patient 1 (f), patient 3 (g) and patient 4 (h) were all stop gain mutations, causing the lost of the helix richc-terminal part of the SPG11, which could be important for structural stabilization