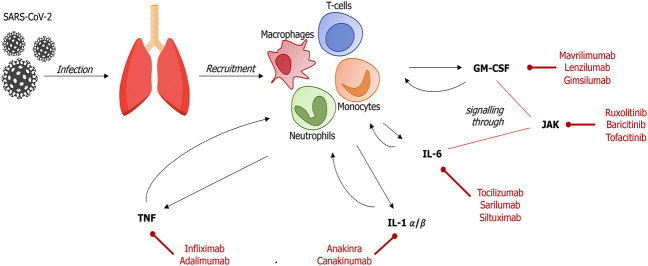
FIGURE 1.
Main pathways and treatment targets in SARS-CoV-2–induced immune response In the early stage of SARS-CoV-2 infection, infected cells and resident macrophages release signaling molecules that recruit host immune cells into the alveolar space. These cells, mainly neutrophils, T-lymphocytes and monocytes, produce and release high levels of inflammatory cytokines, leading to an uncontrolled inflammatory response (GM-CSM, granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; JAK, Janus kinase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor).