Figure 5.
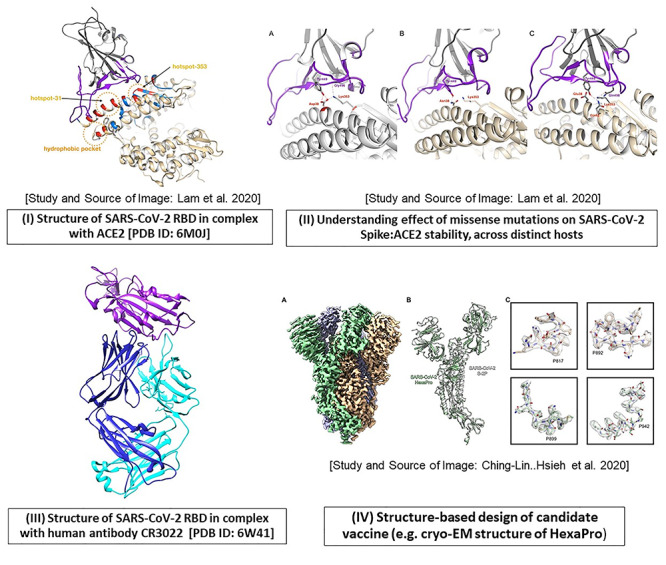
An account of structure-based studies on spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2. Some of the applications using spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 are illustrated, as follows. (I) The crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD; shown in purple) in complex with human ACE2 receptor (gray) is depicted using Chimera [PDB ID: 6M0J]. The direct contact residues (shown in red while residues in secondary shell are shown in blue) as well as key hotspot positions 31 and 353 (encircled in orange) are studied by various groups [6, 7]. (II) The impact of mutations at hotspot residue 353, on the stability of the RBD-ACE2 complex in various hosts (A. human, B. horseshoe bat, C. cat and dog) are illustrated (Source of images (I) and (II) and more details in Lam et al. [124]). (III) The crystal structure of RBD (purple) in complex with human antibody CR3022 (heavy chain: blue, light chain: cyan) is resolved (PDB ID: 6W41). (IV) Structure-based design of prefusion conformation of spike: design of vaccine candidate namely HexaPro: the high resolution cryo-EM structure is solved by Hsieh et al. [18]; Source of Image: Hsieh et al. [18].
